Mixing Xanax and Alcohol
Mixing Xanax and alcohol is harmful due to their combined effects on the central nervous system. Both substances enhance the depressant effects, leading to excessive sedation, drowsiness, and impaired cognitive and motor functions. This can increase the risk of accidents, falls, and injuries. Furthermore, combining Xanax and alcohol can lead to severe respiratory depression, where breathing becomes shallow or slowed, potentially leading to respiratory failure or death.
Long-term consequences of combined Xanax and alcohol use include cardiovascular, gastrointestinal, hepatic, kidney, and neurologic injury and worsening psychiatric conditions.
The interaction between the two substances also increases the risk of blackouts, memory loss, and impaired judgment. Xanax and alcohol can cause liver toxicity individually, and their combination further strains the liver, potentially leading to liver damage. It is crucial to avoid mixing Xanax and alcohol to prevent these dangerous outcomes and protect one’s well-being.
Xanax and Alcohol Mechanism of Action
Xanax (brand name for alprazolam) and alcohol have distinct mechanisms of action, but both affect the (CNS) central nervous system. Xanax belongs to a class of drugs called benzodiazepines, which work by enhancing the effects of a neurotransmitter called gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA). GABA is responsible for inhibiting or reducing the activity of nerve cells, resulting in sedative, anxiolytic (anti-anxiety), and muscle-relaxing effects.
Alcohol, on the other hand, has a multifaceted mechanism of action. It affects multiple brain neurotransmitter systems, including GABA, glutamate, dopamine, and serotonin. Alcohol enhances the effects of GABA, similar to Xanax, leading to sedation and relaxation. It also inhibits the activity of the excitatory neurotransmitter glutamate, resulting in further central nervous system depression.
Xanax and Alcohol Interactions
When Xanax and alcohol are combined, their effects become additive or synergistic. Both substances potentiate the depressant effects of GABA and increase sedation and relaxation. This can lead to intensified central nervous system depression, including excessive sedation, impaired coordination, and cognitive impairment. The combined effects also increase the risk of respiratory depression and the potential for overdose.
What Happens If You Mix Xanax and Alcohol?
Mixing Xanax and alcohol can have severe and potentially life-threatening consequences. Some potential outcomes of mixing Xanax and alcohol include the following:
Xanax and Alcohol Effects
- Increased sedation.
- Xanax and alcohol depress the central nervous system, and their combination intensifies sedative effects. This can result in extreme drowsiness, confusion, and difficulty staying awake.
- Impaired motor function.
- Mixing Xanax and alcohol can severely impair coordination, balance, and motor skills, making it dangerous to drive, operate machinery, or do activities requiring alertness.
- Respiratory depression.
- Combining Xanax and alcohol can cause respiratory depression, where breathing becomes shallow or slowed. This can lead to oxygen deprivation and potentially life-threatening complications such as respiratory failure.
- Memory loss and blackouts.
- The combined use of Xanax and alcohol can increase the risk of memory loss or blackouts. Individuals may have gaps in their memory and cannot recall events during substance use.
- Increased overdose risk.
- Mixing Xanax and alcohol significantly increases the risk of overdose. Both substances depress the central nervous system, and their combined effects can suppress vital functions to dangerous levels. Overdose symptoms may include severe drowsiness, slowed breathing, loss of consciousness, and even coma.

Skip To:
Learn More:
- Is Xanax Addictive? Signs, Effects & Treatment
- How Long Does Xanax Stay In Your System?
- What Does Xanax Look Like? What Does a Xanax Pill Look Like? White Xanax Bars, Blue Xanax Bars, Green Xanax Bars, Yellow Xanax Bars…
- Xanax Dosages, Strengths, Interactions, & Forms
- How To Sober Up? Are There Fast Ways To Sober Up From Alcohol?
- How Long Does Alcohol Stay In Your Blood?
- How Long Does Alcohol Stay In Your System? Blood, Urine, & Breathalyzer Test
- Alcohol Use Disorder Symptoms
- Risks of Mixing Prescription Drugs With Alcohol
- Prescription Drugs Addiction Causes & Symptoms
Xanax and Alcohol Overdose
If someone is suspected of overdosing on Xanax and alcohol, it is crucial to seek emergency medical attention immediately. Contacting local emergency services or a poison control center can guide what steps to take.
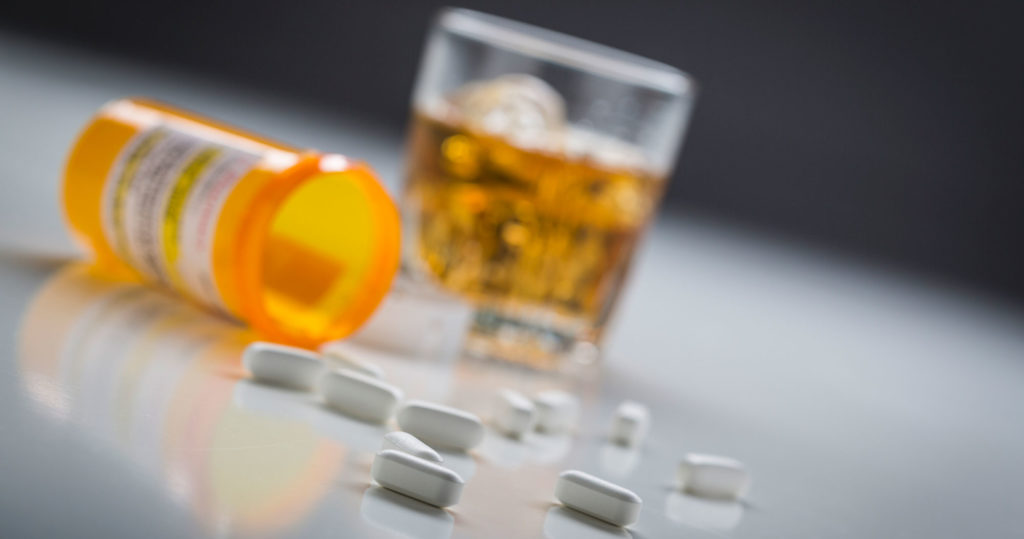
Symptoms of a Xanax and alcohol overdose may include:
- Extreme sedation.
- Confusion.
- Dizziness.
- Slowed or shallow breathing.
- Loss of coordination.
- Blurred vision.
- Unconsciousness.
- In severe cases, an overdose can result in respiratory failure, cardiac arrest, or even death.
To prevent overdose and ensure personal safety, it is strongly advised to avoid mixing Xanax and alcohol altogether and to follow medical advice regarding the appropriate use.
Xanax & Alcohol Drug Facts
Understanding Xanax
Xanax is a brand name for alprazolam, which belongs to a class of medications known as benzodiazepines. It is primarily prescribed to treat:
- Anxiety disorders.
- Panic disorders.
- Anxiety associated with depression.
Xanax functions by enhancing the effects of a neurotransmitter called gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) in the brain, which helps to lower anxiety and promote relaxation.
It is available in immediate-release and extended-release formulations. Xanax is a controlled drug due to its potential for abuse and dependence. It should only be used under the guidance and prescription of a healthcare professional, and the dosage should be carefully monitored to minimize the risk of adverse effects.
Prolonged or excessive use of Xanax can lead to tolerance, dependence, withdrawal symptoms upon discontinuation, and potential misuse or addiction.
Mixing Xanax With Alcohol Warnings
The combined side effects of Xanax and alcohol can lead to excessive sedation, impaired coordination, and respiratory depression. This can result in accidents, injuries, and even respiratory failure. The combination also increases the risk of memory loss, blackouts, and impaired judgment, leading to risky behaviors and poor decision-making. Moreover, mixing Xanax and alcohol puts extra strain on the liver, potentially leading to liver damage.
Xanax for Alcohol Withdrawal Management
Xanax (alprazolam) can be prescribed to manage alcohol withdrawal, but it should be done under careful medical supervision. Xanax belongs to the benzodiazepine class, generally prescribed for its sedative and anxiolytic effects. When alcohol-dependent individuals abruptly stop drinking, they may experience withdrawal symptoms, including anxiety, insomnia, tremors, and seizures. Xanax can help alleviate these symptoms by acting on the same brain GABA receptors that alcohol affects.
However, Xanax should be used cautiously and only as part of a comprehensive alcohol withdrawal management plan. It should be prescribed and monitored by a healthcare professional experienced in addiction medicine. The dosage and duration of Xanax treatment should be tailored to the individual’s needs, and a gradual tapering-off process is usually recommended to avoid dependence on Xanax.
Understanding Polysubstance Abuse
Polysubstance abuse involving Xanax and alcohol can lead to memory loss, blackouts, and impaired judgment. This can result in risky behaviors, poor decisions, and experiencing difficulties in daily functioning. Combining Xanax and alcohol also carries a higher risk of addiction and dependence. Both substances can potentially be misused and can lead to physical and psychological dependence when used habitually or in high doses.
Can you mix alcohol and Xanax? No. It is advised to mix both substances. It is crucial to seek professional help and support to address polysubstance abuse involving Xanax and alcohol side effects. Comprehensive treatment approaches, including medical detoxification, counseling, behavioral therapies, and support group gatherings or meetings, are necessary to address the underlying issues and promote recovery.

Get Your Life Back
Find Hope & Recovery. Get Safe Comfortable Detox, Addiction Rehab & Dual Diagnosis High-Quality Care.
Hotline(844) 597-1011Xanax and Alcohol Statistics
Many use Xanax for too long, often with a doctor’s permission. Among patients prescribed Xanax medication, many don’t realize they’re dependent on it until it’s too late—many individuals who take Xanax without a prescription or recreationally describe the feeling as calming or sedating. Often, Xanax is mixed with alcohol for more intense effects.
5.4 Million
In 2019, approximately 5.4 million people aged 12 or older reported misusing prescription tranquilizers, including drugs like Xanax.
Source: NSDUH
0.3%
In 2019, about 0.3% of people aged 12 or older had a benzodiazepine use disorder.
Source: NSDUH
52%
In one study, roughly 52% of the survey participants combined medication with alcohol twice a year, while around 17% combined more than once a week.
Source: NCBI
Can I Drink Alcohol While Taking Xanax?
No, it is not safe to drink alcohol while taking Xanax (alprazolam). Both drugs, Xanax and alcohol, are central nervous system (CNS) depressants and can have additive effects on the body. Unfortunately, conditions like depression, trauma, stressor-related disorders, anxiety disorders, psychotic disorders, bipolar disorder, etc., are more prevalent in people who abuse multiple substances.
The effects of alcohol and Xanax drug interactions are profound and harmful, and dependency on benzodiazepines is a real possibility when not taken by a doctor’s instructions.
When someone develops Xanax dependency, abruptly stopping or reducing the dosage of Xanax can result in withdrawal symptoms, which may include anxiety, insomnia, irritability, tremors, and in severe cases, seizures. It is crucial to work closely with a healthcare professional to taper off the medication and manage withdrawal symptoms safely gradually.
Get Help. Get Better. Get Your Life Back.
Searching for Accredited Drug and Alcohol Rehab Centers Near You?
Even if you have failed previously and relapsed, or are in the middle of a difficult crisis, we stand ready to support you. Our trusted behavioral health specialists will not give up on you. When you feel ready or just want someone to speak to about therapy alternatives to change your life call us. Even if we cannot assist you, we will lead you to wherever you can get support. There is no obligation. Call our hotline today.
(844) 597-1011Alcohol and Xanax Withdrawal Symptoms
Alcohol and Xanax withdrawal symptoms can co-occur, especially in cases where an individual has been using both substances concurrently or has developed a dependence on both alcohol and Xanax.
Alcohol dependency can lead to physical and psychological dependence, where the body and mind rely on alcohol to function normally. Concomitant and heavy alcohol consumption can lead to tolerance, meaning more significant amounts of alcohol are needed to achieve the desired effect. If someone dependent on alcohol discontinues, they experience withdrawal. Common alcohol withdrawal symptoms may include:
- Tremors (shakes): Uncontrollable shaking of the hands, arms, or other body parts.
- Anxiety and irritability: Feelings of restlessness, nervousness, and heightened irritability.
- Insomnia: Difficulty falling asleep or staying asleep.
- Nausea and vomiting: Upset stomach, feeling queasy, and vomiting.
- Sweating: Excessive sweating, even without physical exertion.
- Headache: Persistent headaches and migraines.
- Increased heart rate: Rapid or irregular heartbeat.
- Elevated blood pressure: High blood pressure levels.
- Mood swings: Emotional instability, ranging from sadness to agitation.
- Hallucinations and seizures: In severe cases, alcohol withdrawal can lead to hallucinations (visual or auditory) and even seizures.
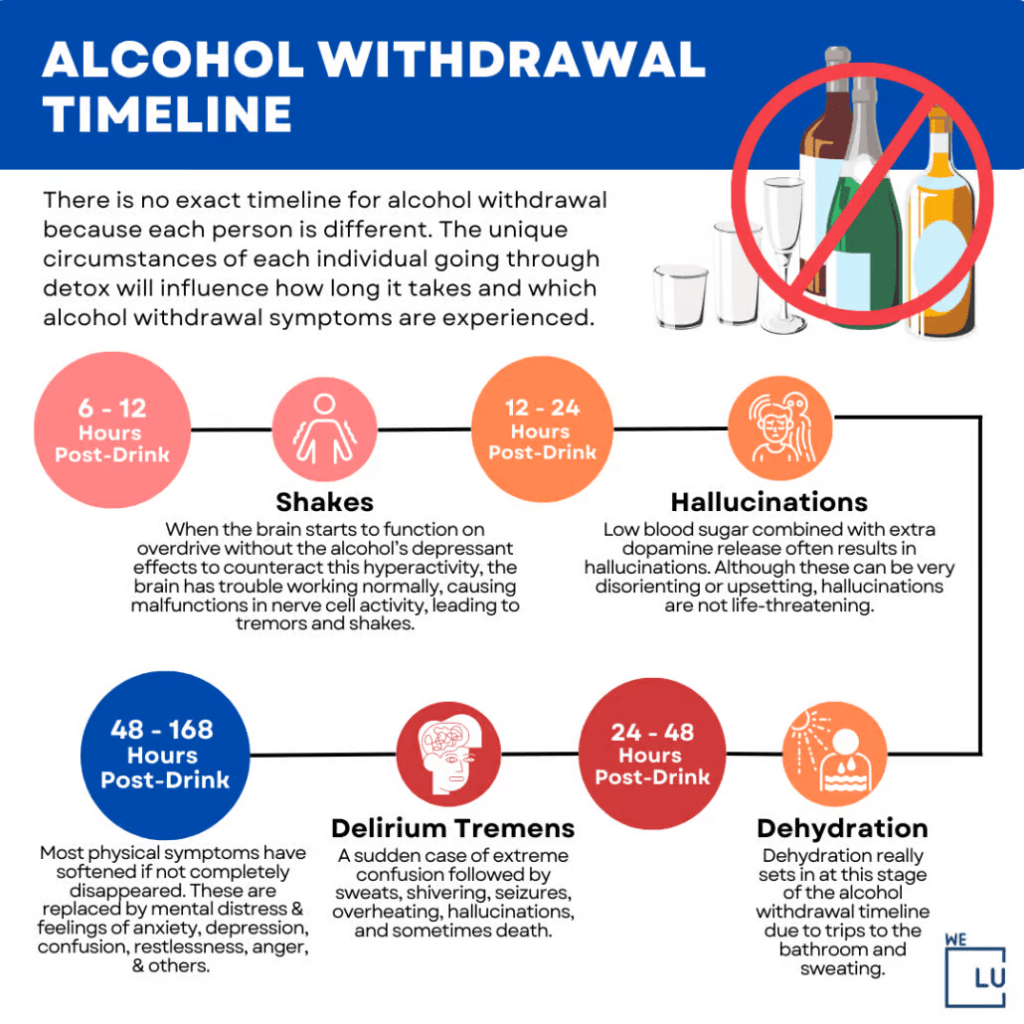
Alcohol Withdrawal Timeline Infographic
Due to the potential for severe withdrawal signs and symptoms, including seizures and delirium tremens (a severe form of alcohol withdrawal), it is crucial to seek medical supervision and assistance when discontinuing alcohol and Xanax use.
Embed the below “Alcohol Withdrawal Timeline” Infographic to your Website. This alcohol withdrawal timeline infographic is provided by the We Level Up addiction treatment center team. To use the above infographics, you agree to link back and attribute its source and owner at https://welevelup.com/addiction/xanax-and-alcohol/
Alcohol Withdrawal Timeline infographic image link: https://welevelup.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/03/Stages-Of-Alcohol-Withdrawal-Timeline-2-1030×1030-1-1024×1024.png
Xanax Withdrawal Symptoms
Xanax withdrawal symptoms can occur when a person stops or significantly reduces their use of Xanax (alprazolam) after prolonged or high-dose use. Common Xanax withdrawal symptoms may include:
- Anxiety and panic attacks: Heightened anxiety levels, restlessness, and panic episodes.
- Insomnia: Difficulty falling asleep or staying asleep.
- Muscle pain and stiffness: Generalized body aches, muscle tension, and discomfort.
- Headaches: Persistent headaches and migraines.
- Tremors and shaking: Involuntary trembling of the hands, arms, or other body parts.
- Sweating and increased heart rate: Excessive sweating and a rapid or irregular heartbeat.
- Gastrointestinal issues: Nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, or stomach cramps.
- Sensory disturbances: Increased sensitivity to light, sound, or touch.
- Cognitive difficulties: Difficulty concentrating, memory problems, and confusion.
- Mood changes: Mood swings, irritability, and depression.
Alcohol and Xanax withdrawal symptoms can be severe and sometimes life-threatening. It is recommended to seek medical supervision and assistance when discontinuing alcohol or Xanax use to ensure a safe withdrawal process and appropriate management of symptoms.
First-class Facilities & Amenities
World-class High-Quality Addiction & Mental Health Rehabilitation Treatment
Rehab Centers TourRenowned Addiction Centers. Serene Private Facilities. Inpatient rehab programs vary.
Addiction Helpline(844) 597-1011Proven recovery success experience, backed by a Team w/ History of:
15+
Years of Unified Experience
100s
5-Star Reviews Across Our Centers
10K
Recovery Success Stories Across Our Network
- Low Patient to Therapist Ratio
- Onsite Medical Detox Center
- Comprehensive Dual-Diagnosis Treatment
- Complimentary Family & Alumni Programs
- Coaching, Recovery & Personal Development Events
Alcohol and Xanax Polysubstance Abuse Treatment
Treating polysubstance abuse involving alcohol and Xanax (alprazolam) typically involves a comprehensive approach tailored to the individual’s needs. Consulting with a healthcare professional or addiction specialist for a personalized treatment plan is critical. Here are the top components that may be involved in the treatment of alcohol and Xanax polysubstance abuse:
- Medical Detoxification: In cases of severe alcohol and Xanax dependence, medical detoxification in a supervised setting may be necessary. This involves gradually tapering off the substances under medical supervision to manage withdrawal symptoms and minimize the risk of complications.
- Medication-Assisted Treatment (MAT): Medications may be prescribed to help manage withdrawal symptoms and cravings. For example, specific medications can be used to address alcohol withdrawal symptoms or support benzodiazepine tapering in a controlled manner.
- Psychotherapy: Individual or group therapy sessions are often used to address underlying issues contributing to substance abuse and to develop coping strategies and relapse prevention skills. Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) and motivational enhancement therapy (MET) are commonly employed.
- Support Groups: Participation in support groups like Alcoholics Anonymous (AA) or other addiction support groups can provide a supportive network of individuals going through similar challenges, offer guidance, and reinforce recovery efforts.
- Xanax Alcohol Dual Diagnosis Treatment: An integrated treatment for both conditions may be necessary if a person has a co-occurring mental health disorder alongside polysubstance abuse. This could involve therapy, medication management, and collaborative care between mental health and addiction specialists.
- Lifestyle Changes and Skills Building: Positive lifestyle changes, such as adopting healthy coping mechanisms, practicing stress management techniques, improving sleep habits, and engaging in healthy activities, can support long-term recovery.
- Aftercare and Continuing Support: Ongoing support is crucial to maintain sobriety after treatment. This may involve regular check-ins with healthcare professionals, participation in relapse prevention programs, and continued engagement in support groups.
Treatment approaches may vary based on individual circumstances, and a tailored treatment plan should be developed in consultation with healthcare professionals. Recovery from polysubstance abuse can be challenging, but long-term sobriety is possible with proper support, resources, and commitment.
Contact We Level Up addiction treatment center for more personalized treatment options and approaches. Get FREE addiction treatment insurance check – https://welevelup.com/rehab-insurance/ If you or a loved one is struggling with Xanax and alcohol addiction or other substance use disorder(s), call for a FREE consultation 24/7 at (561) 678-0917
World-class, Accredited, 5-Star Reviewed, Effective Addiction & Mental Health Programs. Complete Behavioral Health Inpatient Rehab, Detox plus Co-occuring Disorders Therapy.
CALL(844) 597-1011End the Addiction Pain. End the Emotional Rollercoaster. Get Your Life Back. Start Drug, Alcohol & Dual Diagnosis Mental Health Treatment Now. Get Free No-obligation Guidance by Substance Abuse Specialists Who Understand Addiction & Mental Health Recovery & Know How to Help.
Top 3 Alcohol and Xanax FAQs
-
What is worse for your liver alcohol or Xanax?
Alcohol is generally considered worse for the liver compared to Xanax. Chronic alcohol use can damage the liver, including inflammation (alcoholic hepatitis), fatty liver disease, and cirrhosis. Alcohol use disorder is one of the leading causes of liver disease. While Xanax can potentially cause liver toxicity, it is rare and occurs primarily with high doses or prolonged use. Alcohol Xanax combination should be avoided. The prescription drug should be used cautiously, and individuals should follow medical advice and avoid excessive or prolonged use to protect their liver health.
-
Can you drink alcohol with Xanax?
It is not recommended to drink alcohol while taking Xanax. May it be 25 mg Xanax and alcohol or even the smallest dosage of Xanax. Xanax and alcohol are central nervous system (CNS) depressants and can enhance each other’s effects, leading to excessive sedation, impaired coordination, and increased risk of accidents or overdose. Combining alcohol and Xanax can also heighten the risk of respiratory depression, a life-threatening emergency. Moreover, both alcohol and Xanax can cause liver toxicity, and their combination may further strain the liver. It is crucial to follow medical advice and avoid alcohol consumption while taking Xanax to ensure your safety and well-being.
-
What happens when you mix Xanax and alcohol?
Mixing Xanax and alcohol can have detrimental consequences. Both substances are central nervous system depressants, and combining them can intensify their sedative effects. This can lead to severe drowsiness, dizziness, impaired coordination, and confusion. The combination increases the risk of accidents, falls, and injuries. Moreover, it can also cause respiratory depression, potentially leading to difficulty breathing or even respiratory failure. Mixing Xanax and alcohol can be life-threatening and should be avoided to ensure safety.
Alcohol Withdrawal Timeline Symptoms, Stages, Syndrome, Medication, Risks & Treatment
Withdrawal from Xanax and alcohol can be detrimental and potentially life-threatening if not managed properly. Both substances affect the central nervous system, and abruptly stopping their use can lead to severe withdrawal signs and symptoms such as hallucinations, seizures, and delirium tremens.
Treatment for Xanax and alcohol withdrawal typically involves medical supervision and may include medications to alleviate symptoms and prevent complications. Gradual tapering of the doses of these substances under medical care is often recommended to minimize withdrawal symptoms. It is crucial to seek professional help and support from healthcare providers when dealing with Xanax and alcohol withdrawal to ensure safety and successful recovery.
How long does alcohol withdrawal last? Watch the below video for further details. Mixing alcohol and Xanax can worsen each withdrawal symptom and affect recovery duration.
Alcohol Withdrawal Timeline Symptoms & Treatment Video Transcript.
Welcome to the We Level Up treatment center video series. In today’s video, we will discuss Alcohol Withdrawal Timeline Symptoms, Stages, Syndrome, Medication, Risks & Treatment Options
When you stop drinking, alcohol withdrawal timeline symptoms like jumpiness, tremors, dehydration & anxiety can be expected. The severity of alcohol detox withdrawal treatment can be felt within hours of discontinuing drinking.
Alcohol withdrawal symptoms happen when someone drinking too much alcohol regularly suddenly stops drinking. The more a person drinks regularly, the more likely they will develop alcohol withdrawal symptoms when they stop drinking. According to the National Institute of Health, Alcohol withdrawal symptoms include difficulty sleeping, alcohol cravings, reduced energy, and feeling depressed or low.
When Does the Timeline for Alcohol Withdrawal Symptoms Begin?
In most cases, withdrawal from alcohol mild symptoms may begin to develop within hours of the last alcoholic beverage consumed. Alcohol withdrawal has a broad range of symptoms, from mild tremors to a severe condition called delirium tremens, which results in seizures and could progress to death if not recognized and treated promptly.
What are the Major Alcohol Withdrawal Timeline Symptoms?
Alcohol withdrawal timeline symptoms describe what happens to your brain and body when you get dependent on alcohol and stop suddenly. Likewise, the alcohol withdrawal timeline examines the signs of alcohol withdrawal. When searching for the “timeline quit drinking” and the time frame for symptoms of alcohol detox, you will note the symptoms are the same.
If you or a loved one is suffering from alcohol withdrawal, begin by learning more about the withdrawal process. Discover what to expect from alcohol withdrawal treatment and which therapies suit you. Explore the alcohol withdrawal timeline symptoms and potential effects of alcohol abstinence. Learn what delirium tremens (DTs) are, plus the effects of alcohol withdrawal on mental health. Keep in mind that alcohol detox should consider that:
Alcohol withdrawal can be uncomfortable, risky, and even lethal without proper professional detox treatment. More so if the patient is a heavy drinker for a longer period.
Alcohol withdrawal symptoms include anxiety, tremors, sweating, and nausea. More severe alcohol withdrawal symptoms include fever, mental confusion, and seizures.
The safer method to detox from alcohol is under properly supervised medical alcohol detox treatment.
Experience Transformative Recovery at We Level Up Treatment Centers.
See our authentic success stories. Get inspired. Get the help you deserve.
Start a New Life
Begin with a free call to an addiction & behavioral health treatment advisor. Learn more about our dual-diagnosis programs. The We Level Up Treatment Center Network delivers recovery programs that vary by each treatment facility. Call to learn more.
- Personalized Care
- Caring Accountable Staff
- World-class Amenities
- Licensed & Accredited
- Renowned w/ 100s 5-Star Reviews
We’ll Call You
Search We Level Up Xanax and Alcohol Detox, Mental Health Topics & Resources
Sources:
[1] Ait-Daoud N, Hamby AS, Sharma S, Blevins D. A Review of Alprazolam Use, Misuse, and Withdrawal. J Addict Med. 2018 Jan/Feb;12(1):4-10. DOI: 10.1097/ADM.0000000000000350. PMID: 28777203; PMCID: PMC5846112.
[2] Physician Office Visits at Which Benzodiazepines Were Prescribed: Findings From 2014–2016 National Ambulatory Medical Care Survey – Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC)
[3] Huang Z, Xu Z, Wang H, Zhao ZQ, Rao Y. Influence of ethanol on the metabolism of alprazolam. Expert Opin Drug Metab Toxicol. 2018 Jun;14(6):551-559. DOI 10.1080/17425255.2018.1483338. PMID: 29848078.
[4] George TT, Tripp J. Alprazolam. [Updated 2023 Apr 24]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2023 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK538165/
[5] XANAX® alprazolam tablets, USP – Accessdata.fda.gov
[6] Alprazolam: MedlinePlus Drug Information – Available from: https://medlineplus.gov/druginfo/meds/a684001.html
[7] Drug Fact Sheet: Benzodiazepines – Drug Enforcement Administration (DEA)
[8] Hirschtritt ME, Palzes VA, Kline-Simon AH, Kroenke K, Campbell CI, Sterling SA. Benzodiazepine and unhealthy alcohol use among adult outpatients. Am J Manag Care. 2019 Dec 1;25(12):e358-e365. PMID: 31860229; PMCID: PMC7217068.
[9] Linnoila MI. Benzodiazepines and alcohol. J Psychiatr Res. 1990;24 Suppl 2:121-7. doi 10.1016/0022-3956(90)90043-p. PMID: 1980691.
[10] Abernethy DR, Greenblatt DJ, Ochs HR, Shader RI. Benzodiazepine drug-drug interactions commonly occur in clinical practice. Curr Med Res Opin. 1984;8 Suppl 4:80-93. doi 10.1185/03007998409109546. PMID: 6144465.



