What is Hangxiety?
“Hangxiety” is a colloquial term that describes the combination of hangover symptoms, such as headache, fatigue, and nausea, along with heightened anxiety or feelings of unease after consuming alcohol. Hangxiety can be attributed to the effects of alcohol on various neurotransmitter systems in the brain.
Alcohol is a (CNS) central nervous system depressant. Initially, alcohol produces a sedative effect that can temporarily alleviate anxiety. However, as the body metabolizes alcohol and its blood concentration decreases, a rebound effect can lead to withdrawal-like symptoms. This rebound effect may result in increased excitability and anxiety.
Moreover, alcohol can disrupt usual sleep patterns, leading to poor sleep quality. Sleep disturbances can contribute to feelings of anxiety and irritability the next day, exacerbating hangover-related anxiety symptoms.
While the scientific understanding of hangxiety is still evolving, it is generally attributed to the complex interplay of alcohol’s effects on neurotransmitters, sleep patterns, and the body’s adjustment to alcohol withdrawal.
What Causes Hangxiety?
Hangxiety, or the experience of heightened anxiety or unease after consuming alcohol, can be caused by several factors:
Alcohol Metabolism
When someone consumes alcohol, the body metabolizes it, releasing toxic compounds called acetaldehyde. This compound, acetaldehyde, causes body inflammation, such as in the pancreas, the liver, the gastrointestinal (GI) tract, and the brain.
This inflammation, combined with dehydration, causes the person to feel sick. As the brain and body try to regain the chemical balance (primarily that of dopamine) after excessive alcohol drinking, there is a chance that one experiences some degree of alcohol withdrawal. These alcohol withdrawal effects can temporarily alter the nervous system and mood, which may mean hangxiety for some. Researchers haven’t identified a single cause. But have proposed several theories.
Alcohol-Related Actions
In some situations, hangover anxiety results from a person’s actions rather than alcohol. One may feel anxious if they are unable to recall what happened after an excessive amount of drinking. Decreased cognitive function, typical during a hangover, can lead to a lower ability to make good decisions and thus may result in anxiety when later reflected upon.
Alcohol Sleep Disruption
Alcohol can disrupt normal sleep patterns, leading to poor sleep quality. Even though alcohol may initially make you feel drowsy and help you fall asleep, it can disturb the later stages of sleep, particularly rapid eye movement (REM) sleep. REM sleep is crucial for restorative sleep and emotional regulation. Sleep disturbances can contribute to feelings of anxiety and unease the next day, intensifying hangxiety symptoms.
Hangxiety Due To Neurotransmitter Imbalances
Alcohol affects the levels of brain neurotransmitters, including gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) and glutamate. GABA inhibitory neurotransmitter helps regulate moods, such as anxiety, while glutamate is an excitatory neurotransmitter associated with increased brain activity. Excessive alcohol consumption can disrupt the balance between these neurotransmitters, increasing anxiety during and after alcohol consumption.
Alcohol Withdrawal
Hangxiety can be a manifestation of these withdrawal symptoms as the body readjusts to the absence of alcohol.
When the effects of alcohol wear off, especially after heavy or prolonged drinking, the body may go through a withdrawal period. Alcohol withdrawal can cause anxiety symptoms, including restlessness, irritability, and nervousness.
Pre-Existing Anxiety Disorders
Individuals with pre-existing anxiety disorders may be more susceptible to experiencing hangxiety. Alcohol can exacerbate anxiety symptoms in those already prone to anxiety, disrupting the natural balance of neurotransmitters and affecting overall emotional regulation.

Skip To:
Learn More:
- Strong Connection Between Alcohol and Anxiety
- Dangers of Mixing Sleeping Pills and Alcohol
- Links Between Alcohol and Insomnia Problems
- What are the 3 Stages of Addiction? Alcoholism Explained
- Alcohol Blackout Signs, Causes, & Dangers
- AWS or Alcohol Withdrawal Timeline Symptoms, Seizures, Signs & Alcohol Withdrawal Detox Treatment
- Emotional Effects of Alcohol
- The Dangers of Mixing Alcohol and Anxiety Meds
- Alcohol Detox Timeline & How To Safely Manage Alcohol Withdrawal Symptoms Treatment
- How Long Does Alcohol Stay In Your System? Blood, Urine, & Breathalyzer Test
Alcohol Hangxiety Meaning Fact Sheet
Alcohol and Anxiety Connection
While alcohol is known as a depressant that can initially produce a calming effect, its relationship with anxiety is more complex.
Alcohol affects the neurotransmitter systems in the brain, including gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) and glutamate. GABA inhibitory neurotransmitter regulates anxiety, while glutamate is an excitatory neurotransmitter associated with increased brain activity. Alcohol enhanced the effects of GABA, leading to feelings of relaxation and decreased anxiety initially.
However, as alcohol is metabolized and its concentration in the bloodstream decreases, the balance between GABA and glutamate can be disrupted. This can result in a rebound effect, where glutamate activity is increased, leading to heightened anxiety and irritability. This rebound effect is often experienced as hangxiety, occurring the day after consuming alcohol.
How Long Does Hangxiety Last?
The duration of hangxiety can vary from person to person. Typically, hangxiety occurs during the hangover phase, following alcohol consumption, when the body metabolizes and eliminates alcohol.
Hangxiety can last for several hours or even a whole day. During this time, individuals may experience anxiety, unease, irritability, restlessness, and sometimes even panic. These symptoms can accompany physical discomforts, such as headaches, nausea, and fatigue.
Hangxiety is not a clinical term and is not officially recognized as a medical condition. However, it is a commonly reported phenomenon, and the duration and intensity of hangxiety symptoms can vary among individuals.
How To Get Rid Of Hangxiety?
To alleviate hangxiety symptoms, it’s generally advised to focus on self-care practices such as the following:
- Staying hydrated.
- Getting sufficient rest.
- Engaging in relaxation techniques (e.g., deep breathing, meditation).
- Eating nutritious meals.
- Avoiding further alcohol consumption.
People at Risk of Hangxiety
While hangxiety can affect different individuals in varying degrees, certain factors may increase the risk of experiencing hangxiety:
- Individuals with high levels of stress.
- People experiencing high-stress levels, whether due to work, personal life, or other factors, may find that alcohol exacerbates their anxiety and contributes to hangxiety.
- Individuals with pre-existing anxiety disorders.
- People with anxiety issues, such as generalized anxiety disorder (GAD) or social anxiety disorder (SAD), may be more susceptible to experiencing hangxiety due to alcohol consumption.
- Individuals with a history of depression.
- Those with a history of depression may be more prone to experiencing hangxiety symptoms. Alcohol is a depressant, and its effects on neurotransmitters in the brain can contribute to depressive feelings.
- Individuals who consume alcohol excessively.
- Consuming alcohol in excessive amounts or binge drinking can increase the likelihood of experiencing hangxiety. The higher the alcohol intake, the greater the potential for adverse emotional and physical effects.
- Personal sensitivity to alcohol.
- Some individuals may be more sensitive to the effects of alcohol, including its impact on mood and anxiety. Even small amounts of alcohol can trigger anxiety symptoms in these individuals.
- Genetic factors.
- Genetic factors can influence an individual’s susceptibility to hangxiety. Some people may have genetic variations that make them more prone to experiencing anxiety and related symptoms after alcohol consumption.
Hangxiety can occur in anyone who consumes alcohol, regardless of the above factors.
If you regularly experience hangxiety or if it significantly impacts your well-being, it’s advisable to seek support from an alcohol and mental health expert who can provide appropriate guidance and assistance.

Get Your Life Back
Find Hope & Recovery. Get Safe Comfortable Detox, Addiction Rehab & Dual Diagnosis High-Quality Care.
Hotline(844) 597-1011Alcohol Anxiety-Related Statistics
In some cases, what we think is only hangover anxiety can be a symptom of alcohol withdrawal. Alcohol withdrawal signifies that there is a problem with drinking. Moreover, people with pre-existing mental health conditions are at higher risk of worsening anxiety after drinking.
The co-occurrence of alcohol use disorders and anxiety disorders is well-documented. People with anxiety disorders may be more likely to use alcohol to cope with their signs and symptoms, leading to an increased risk of developing an alcohol use disorder. Moreover, alcohol use can exacerbate anxiety symptoms and contribute to the development of anxiety disorders in susceptible individuals.
40 Million
Around 40 million adults in the US aged 18 and older are impacted by anxiety disorders, which amounts to about 18.1% of the population.
Source: ADAA
15.1 Million
Roughly 15.1 million adults in the US had an alcohol use disorder (AUD) in 2019. Among individuals with AUD, it is common to experience comorbid mental health conditions, including anxiety disorders.
Source: NIAAA
1.3 Million
In 2019, roughly 1.3 million individuals aged 12 or older received treatment for alcohol use disorder (AUD) at specialized facilities in the US.
Source: SAMHSA
Identifying Hangxiety Symptoms
Hangxiety is not a clinically recognized term or condition but rather a slang term used to describe a specific type of anxiety experienced during a hangover.
Hangxiety refers to the feelings of anxiety, unease, or distress that some individuals experience during a hangover, typically after consuming alcohol. The symptoms of hangxiety can vary from person to person, but common manifestations may include:
- Increased anxiety: Hangxiety is characterized by heightened anxiety, nervousness, or restlessness. Individuals may experience a sense of unease or apprehension.
- Irritability: Hangxiety can also lead to irritability and a decreased tolerance for stress or frustration. Small triggers or inconveniences may provoke stronger emotional reactions than usual.
- Racing thoughts: Many individuals with hangxiety report racing thoughts or a rapid flow of ideas. These thoughts may center around self-doubt, regret, embarrassment, or worry about the previous night’s events.
- Rumination: Hangxiety can lead to excessive rumination, with individuals replaying and overanalyzing past interactions or situations. They may dwell on perceived social or personal mistakes, creating a cycle of negative thoughts.
- Physical discomfort: In addition to psychological symptoms, hangxiety can be accompanied by physical discomfort. Headaches, fatigue, nausea, and general malaise are common complaints during a hangover, contributing to overall feelings of unease.
- Social withdrawal: Some individuals with hangxiety may feel inclined to isolate themselves and avoid social interactions. They may fear judgment or be concerned about their ability to navigate social situations while experiencing heightened anxiety.
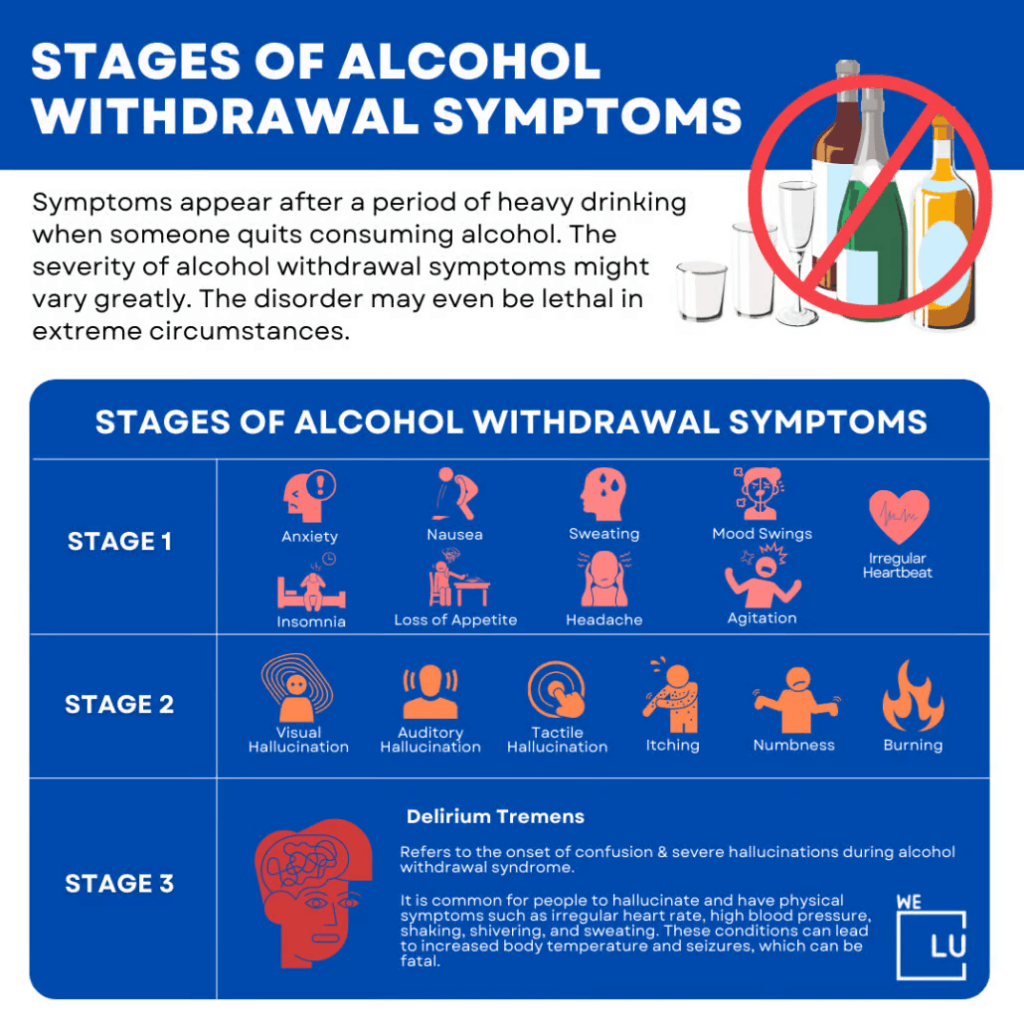
Stages of Alcohol Withdrawal Symptoms Infographic
Anxiety can manifest at different stages during alcohol withdrawal, and the onset and severity of anxiety symptoms can vary among individuals. Typically, anxiety symptoms can start within a few hours to a few days after the last drink and may peak during the first few days of alcohol withdrawal.
Alcohol withdrawal can range in severity from mild to severe, with severe cases potentially leading to alcohol withdrawal syndrome (AWS), which can include more severe anxiety symptoms and other potentially dangerous symptoms such as hallucinations and seizures. Severe alcohol withdrawal requires medical intervention and should be managed under the care of healthcare professionals.
Embed the below “Stages of Alcohol Withdrawal Symptoms” Infographic to your Website. This stages of alcohol withdrawal symptoms infographic is provided by the We Level Up addiction treatment center team. To use the above infographics, you agree to link back and attribute its source and owner at https://welevelup.com/addiction/hangxiety/
Stages of Alcohol Withdrawal Symptoms infographic image link: https://welevelup.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/03/Stages-Of-Alcohol-Withdrawal-Timeline-1-1030×1030-1-1024×1024.png
Get Help. Get Better. Get Your Life Back.
Searching for Accredited Drug and Alcohol Rehab Centers Near You?
Even if you have failed previously and relapsed, or are in the middle of a difficult crisis, we stand ready to support you. Our trusted behavioral health specialists will not give up on you. When you feel ready or just want someone to speak to about therapy alternatives to change your life call us. Even if we cannot assist you, we will lead you to wherever you can get support. There is no obligation. Call our hotline today.
(844) 597-1011Does Alcohol Cause Anxiety?
Yes. Chronic alcohol drinking can contribute to the development of anxiety disorders. Excessive and prolonged alcohol consumption can disrupt the brain’s chemistry, affect neurotransmitter systems involved in anxiety regulation, and contribute to brain structure and function changes. Over time, this can heighten the risk of developing anxiety disorders, such as (GAD) generalized anxiety disorder or panic disorder. Individuals with pre-existing anxiety disorders may find that alcohol worsens their anxiety symptoms.
While alcohol may temporarily relieve anxiety symptoms for some individuals, relying on alcohol as a coping mechanism can lead to a vicious cycle. Alcohol use can exacerbate anxiety in the long run, and excessive drinking can negatively affect mental health and overall well-being.
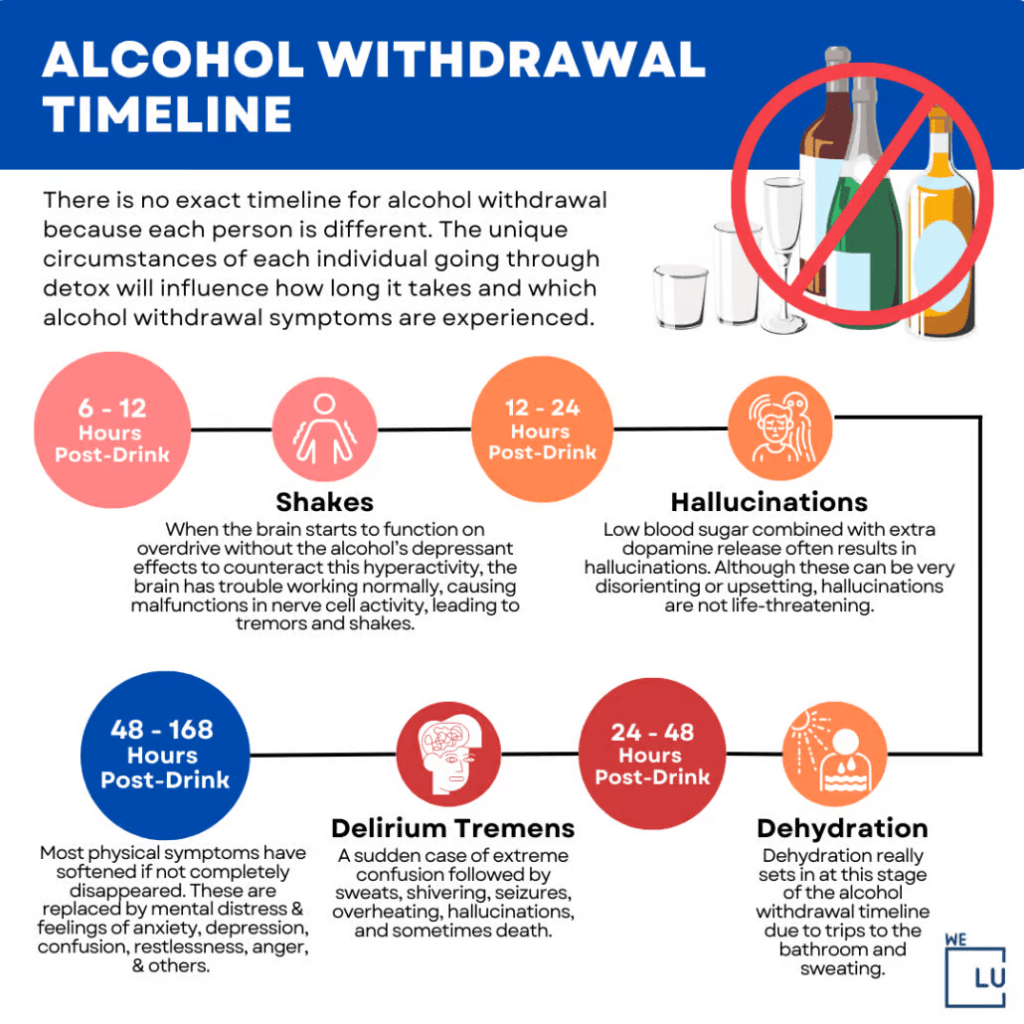
Alcohol Withdrawal Timeline Infographic
The timeline and progression of anxiety symptoms during alcohol withdrawal can be influenced by factors such as the duration and severity of alcohol use, individual differences, and underlying mental health conditions.
Embed the below “Alcohol Withdrawal Timeline” Infographic to your Website. This alcohol withdrawal timeline infographic is provided by the We Level Up addiction treatment center team. To use the above infographics, you agree to link back and attribute its source and owner at https://welevelup.com/addiction/hangxiety/
Alcohol Withdrawal Timeline infographic image link: https://welevelup.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/03/Stages-Of-Alcohol-Withdrawal-Timeline-2-1030×1030-1-1024×1024.png
First-class Facilities & Amenities
World-class High-Quality Addiction & Mental Health Rehabilitation Treatment
Rehab Centers TourRenowned Addiction Centers. Serene Private Facilities. Inpatient rehab programs vary.
Addiction Helpline(844) 597-1011Proven recovery success experience, backed by a Team w/ History of:
15+
Years of Unified Experience
100s
5-Star Reviews Across Our Centers
10K
Recovery Success Stories Across Our Network
- Low Patient to Therapist Ratio
- Onsite Medical Detox Center
- Comprehensive Dual-Diagnosis Treatment
- Complimentary Family & Alumni Programs
- Coaching, Recovery & Personal Development Events
How To Stop Hangxiety?
Experiencing hangxiety, the combination of hangover symptoms and heightened anxiety can be an uncomfortable and distressing experience for individuals who have consumed alcohol. Fortunately, some strategies can help alleviate hangxiety and promote a smoother recovery after drinking.
These suggestions are general and may not apply to everyone. If hangxiety symptoms persist or significantly impact daily life, seeking professional guidance from an alcohol and mental health professional is advised.
Hangxiety Cure Tips
How to cure hangxiety? While there is no definitive “cure” for hangxiety, here are some tips that may be helpful:
- Stay hydrated: Alcohol can dehydrate the body, so drinking plenty of water is essential to rehydrate and flush out toxins. Adequate hydration can help reduce symptoms of both hangovers and anxiety.
- Practice self-care: Engage in activities that promote relaxation and well-being. This may include taking a warm bath, practicing deep breathing techniques, listening to calming music, or engaging in gentle physical exercises such as walking or yoga.
- Get sufficient rest: Allow your body to recover by getting enough sleep. Resting and giving yourself time to relax can help reduce anxiety and improve overall well-being.
- Eat a nutritious meal: Consume a balanced meal with vitamins, minerals, and healthy nutrients. This can help replenish your body and provide energy for recovery.
- Avoid caffeine: While reaching for a cup of coffee may be tempting to counteract fatigue, caffeine can exacerbate anxiety symptoms. Opt for herbal teas or decaffeinated options instead.
- Practice mindfulness or meditation: Mindfulness techniques can help calm the mind and reduce anxiety. Apps or guided meditation videos can be valuable tools for beginners.
- Limit alcohol consumption: If hangxiety is recurring, consider reducing or moderating your alcohol intake. This can help minimize the frequency and intensity of hangover symptoms, including anxiety.
- Seek support: Reach out to friends, loved ones, or support groups for understanding and encouragement. Talking about your experiences can provide a sense of relief and connection.
- Consider professional help: If your anxiety and alcohol side effects persist or significantly impact your daily life, seeking help from an alcohol treatment professional or mental health provider may be beneficial.
Everyone is different, and what works for one person may not work for another. Listening to your body, caring for yourself, and making choices supporting your well-being are crucial.
If you cannot stop drinking and it is causing you significant anxiety, seeking professional help and entering a rehabilitation treatment program can provide the necessary support and resources to address the alcohol dependency and the associated anxiety, leading to a healthier and more balanced life.
Alcohol use Disorder and Hangxiety Treatment
To manage hangxiety, it is crucial to address the immediate symptoms and any underlying anxiety. Developing healthy coping mechanisms for anxiety, such as relaxation techniques, mindfulness, or deep breathing exercises, can help alleviate symptoms. Seeking therapy, such as cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), can assist in addressing the underlying anxiety triggers and provide tools to manage anxiety more effectively.
If you are struggling with alcohol drinking and finding it difficult to control or stop it, seeking rehab treatment can provide a structured and supportive environment for long-term recovery.
Rehab programs offer a range of services, including detoxification, individual and group therapy, educational sessions, and aftercare support, all aimed at addressing the underlying issues related to alcohol use disorder and promoting sustained sobriety.
Professional guidance and a comprehensive treatment plan can significantly increase your chances of achieving long-lasting recovery from alcohol addiction. Contact We Level Up alcohol rehab center today to get started!
World-class, Accredited, 5-Star Reviewed, Effective Addiction & Mental Health Programs. Complete Behavioral Health Inpatient Rehab, Detox plus Co-occuring Disorders Therapy.
CALL(844) 597-1011End the Addiction Pain. End the Emotional Rollercoaster. Get Your Life Back. Start Drug, Alcohol & Dual Diagnosis Mental Health Treatment Now. Get Free No-obligation Guidance by Substance Abuse Specialists Who Understand Addiction & Mental Health Recovery & Know How to Help.
Top 3 Hangxiety Definition FAQs
-
Can alcohol cause anxiety?
Yes, alcohol can cause anxiety. While alcohol is a CNS (central nervous system) depressant that can initially induce feelings of relaxation and euphoria, excessive or long-term alcohol consumption can have the opposite effect. Alcohol disrupts the brain’s neurotransmitter systems, including those involved in anxiety regulation, leading to increased anxiety symptoms. Moreover, alcohol can interfere with sleep patterns, worsen pre-existing anxiety disorders, and contribute to a cycle of alcoholism.
-
How to deal with hangxiety?
If hangxiety becomes overwhelming or significantly impacts your daily living, consider seeking assistance from a mental health and alcohol treatment professional. They can provide guidance and therapy and potentially recommend techniques or medications to manage anxiety symptoms effectively.
-
How to get over hangxiety?
To get over hangxiety, it’s crucial to allow time for your body and mind to recover. Focus on self-care practices such as getting plenty of rest, hydrating, eating nutritious meals, engaging in relaxing activities, and practicing stress-reducing techniques like deep breathing or meditation. If symptoms persist or become overwhelming, consider seeking guidance from an alcohol addiction treatment center that can provide help both for anxiety and the effects of alcohol use disorder.
Alcohol Withdrawal Timeline Symptoms, Stages, Syndrome, Medication, Risks & Treatment
When a person regularly consumes alcohol and suddenly stops or significantly reduces their alcohol intake, their body may experience withdrawal symptoms as it adjusts to the absence of alcohol. Anxiety is a common sign of alcohol withdrawal and can manifest in various ways, such as restlessness, irritability, nervousness, or a sense of impending doom.
Severe alcohol withdrawal symptoms, including delirium tremens (DTs), can also occur in some cases. DTs is a life-threatening condition characterized by extreme confusion, hallucinations, fever, rapid heartbeat, and seizures. If someone is experiencing severe alcohol withdrawal symptoms, seeking medical support as soon as possible is crucial.
If you or a loved one is struggling with alcohol withdrawal or other substance use disorder(s), call for a FREE consultation 24/7 at (561) 678-0917
Get FREE addiction treatment insurance check – https://welevelup.com/rehab-insurance/
Alcohol Withdrawal Timeline Symptoms Video Transcript
Welcome to the We Level Up treatment center video series. In today’s video, we will discuss Alcohol Withdrawal Timeline Symptoms, Stages, Syndrome, Medication, Risks & Treatment Options
When you stop drinking, alcohol withdrawal timeline symptoms like jumpiness, tremors, dehydration & anxiety can be expected. The severity of alcohol detox withdrawal treatment can be felt within hours of discontinuing drinking.
Alcohol withdrawal symptoms happen when someone drinking too much alcohol regularly suddenly stops drinking. The more a person drinks regularly, the more likely they will develop alcohol withdrawal symptoms when they stop drinking. According to the National Institute of Health, Alcohol withdrawal symptoms include difficulty sleeping, alcohol cravings, reduced energy, and feeling depressed or low.
When does the timeline for alcohol withdrawal symptoms begin?
In most cases, withdrawal from alcohol mild symptoms may begin to develop within hours of the last alcoholic beverage consumed. Alcohol withdrawal has a broad range of symptoms, from mild tremors to a severe condition called delirium tremens, which results in seizures and could progress to death if not recognized and treated promptly.
What are the major alcohol withdrawal timeline symptoms?
Alcohol withdrawal timeline symptoms describe what happens to your brain and body when you get dependent on alcohol and stop suddenly. Likewise, the alcohol withdrawal timeline examines the signs of alcohol withdrawal. When searching for the “timeline quit drinking” and the time frame for symptoms of alcohol detox, you will note the symptoms are the same.
If you or a loved one is suffering from alcohol withdrawal, begin by learning more about the withdrawal process. Discover what to expect from alcohol withdrawal treatment and which therapies suit you. Explore the alcohol withdrawal timeline symptoms and potential effects of alcohol abstinence. Learn what delirium tremens (DTs) are, plus the effects of alcohol withdrawal on mental health. Keep in mind that alcohol detox should consider that:
Alcohol withdrawal can be uncomfortable, risky, and even lethal without proper professional detox treatment. More so if the patient is a heavy drinker for a longer period.
Alcohol withdrawal symptoms include anxiety, tremors, sweating, and nausea. More severe alcohol withdrawal symptoms include fever, mental confusion, and seizures.
The safer method to detox from alcohol is under properly supervised medical alcohol detox treatment.
Experience Transformative Recovery at We Level Up Treatment Centers.
See our authentic success stories. Get inspired. Get the help you deserve.
Start a New Life
Begin with a free call to an addiction & behavioral health treatment advisor. Learn more about our dual-diagnosis programs. The We Level Up Treatment Center Network delivers recovery programs that vary by each treatment facility. Call to learn more.
- Personalized Care
- Caring Accountable Staff
- World-class Amenities
- Licensed & Accredited
- Renowned w/ 100s 5-Star Reviews
We’ll Call You
Search We Level Up Hangxiety Alcohol Detox, Mental Health Topics & Resources
Sources
[1] Newman RK, Stobart Gallagher MA, Gomez AE. Alcohol Withdrawal. [Updated 2022 Aug 29]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2023 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK441882/
[2] Alcohol Facts and Statistics – National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism (NIAAA)
[3] Nehring SM, Freeman AM. Alcohol Use Disorder. [Updated 2022 Jul 31]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2023 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK436003/
[4] Alozai Uu, Sharma S. Drug and Alcohol Use. [Updated 2022 Jun 21]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2023 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK513263/
[5] Alcohol use disorder – Available from: https://medlineplus.gov/download/genetics/condition/alcohol-use-disorder.pdf
[5] Mental Health Conditions: Depression and Anxiety Management- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) Available from: https://www.cdc.gov/tobacco/campaign/tips/diseases/depression-anxiety.html
[6] Prevention and Treatment of Anxiety, Depression, and Suicidal Thoughts and Behaviors Among College Students – Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration (SAMHSA)
[7] How To Manage Anxiety? Mental Health and Mental Disorders – Healthy People 2030 Available from: https://health.gov/healthypeople/objectives-and-data/browse-objectives/mental-health-and-mental-disorders
[8] Anxiety Disorders – Office of Women’s Health Available from: https://www.womenshealth.gov/mental-health/mental-health-conditions/anxiety-disorders
[9] Anxiety Management – VA Mental Health – Veterans Affairs Available from: https://www.mentalhealth.va.gov/anxiety/index.asp
[10] Indicators of Anxiety or Depression Based on Reported Frequency of Symptoms During Last 7 Days – Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC)




