Schizophrenia Treatment, Effective Medication Treatments of Schizophrenia & Psychotherapy Treatment of Schizophrenia.
The goals in treating schizophrenia include targeting symptoms, preventing relapse, and increasing adaptive functioning so that the patient can be integrated back into the community. Since patients rarely return to their baseline level of adaptive functioning, both nonpharmacological and pharmacological treatments must be used to optimize long-term outcomes. Continue to read more about schizophrenia therapies and options.
By We Level Up | Editor Yamilla Francese | Clinically Reviewed By Lauren Barry, LMFT, MCAP, QS, Director of Quality Assurance | Editorial Policy | Research Policy | Last Updated: July 4, 2023
Diagnosis and Schizophrenia Treatments
Schizophrenia is a complex condition, and treatment effectiveness can vary from person to person. Regular communication and collaboration with healthcare providers are crucial in managing symptoms, addressing concerns, and ensuring the most effective treatment approach for each individual.
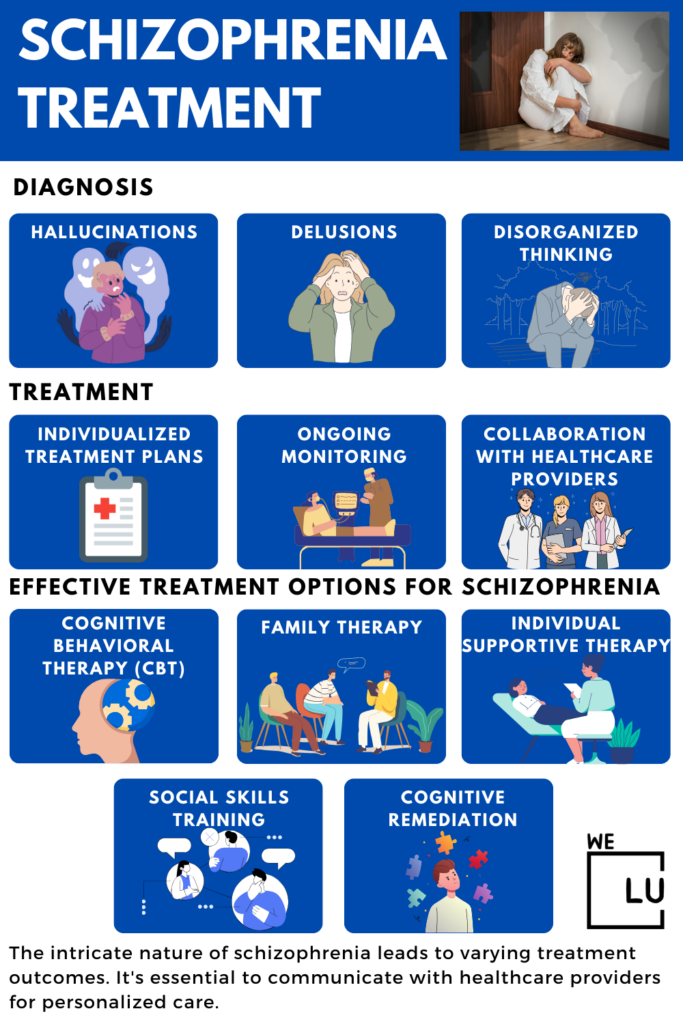
Schizophrenia diagnosis involves evaluating symptoms, such as the following:
- Hallucinations.
- Delusions.
- Disorganized thinking.
- Negative symptoms. Negative symptoms of schizophrenia refer to a reduction or absence of expected behaviors and experiences, such as diminished emotions, social withdrawal, and decreased motivation or pleasure in activities.
Mental health professionals use recognized diagnostic criteria to diagnose accurately. They also consider ruling out other conditions with similar symptoms. The treatment plan is usually tailored to the individual’s specific needs, and ongoing monitoring and adjustments may be necessary to optimize outcomes.
Effective Treatment Options for Schizophrenia
While medication is the primary treatment for managing symptoms, psychotherapy can be beneficial in helping individuals with schizophrenia cope with their condition, improve their functioning, and enhance their overall well-being. Here are some psychotherapy options commonly used in the treatment of schizophrenia:
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT): Cognitive behavioral therapy for schizophrenia aims to identify and change patterns of thinking and behavior contributing to distressing symptoms and difficulties associated with schizophrenia. It focuses on helping individuals challenge and modify irrational beliefs, manage stress, improve problem-solving skills, and enhance coping strategies.
- Family Therapy: Schizophrenia affects the individual and their family members. Family therapy involves the participation of family members to improve communication, resolve conflicts, and develop strategies for supporting the person with schizophrenia. It can help reduce relapse rates and improve family relationships.
- Individual Supportive Therapy: This therapy focuses on establishing a supportive relationship between the therapist and the individual with schizophrenia. It provides a safe space to express their feelings, concerns, and experiences related to their illness. The therapist can offer guidance, validation, and assistance in managing symptoms and daily challenges.
- Social Skills Training: Social skills training aims to improve social interactions, communication, and adaptive functioning in individuals with schizophrenia. It involves teaching specific skills such as assertiveness, problem-solving, emotion regulation, and social cues interpretation. The goal is to enhance interpersonal relationships and promote community integration.
- Cognitive Remediation: Cognitive remediation programs focus on improving cognitive functioning, including attention, memory, and problem-solving abilities, which can be impaired in schizophrenia. These programs use various exercises and techniques to help individuals with schizophrenia enhance their cognitive skills and compensate for deficits.
Above all, the specific type of psychotherapy and its suitability for individuals with schizophrenia can vary based on their symptoms, needs, and preferences.
Intervention Psychosocial Treatments for Schizophrenia
Psychosocial interventions can be used individually or in combination based on the needs and preferences of the individual with schizophrenia.
Here are some intervention-based psychosocial treatments for schizophrenia:
- Assertive Community Treatment (ACT): ACT is a comprehensive, team-based approach that provides intensive and ongoing support to individuals with schizophrenia in the community. A multidisciplinary team, including mental health professionals, case managers, nurses, and social workers, provides various services such as medication management, crisis intervention, housing support, vocational rehabilitation, and social skills training.
- Supported Employment: This approach focuses on helping individuals with schizophrenia find and maintain competitive employment.
- Social Skills Training: Social skills training programs aim to improve social interactions, communication, and adaptive functioning in individuals with schizophrenia.
- Cognitive Enhancement Therapy (CET): CET program aims to enhance cognitive skills such as attention, memory, problem-solving, and social cognition abilities such as perspective-taking and emotion recognition.
- Family-Based Interventions: Involving family members in the treatment process can be crucial for individuals with schizophrenia. Family interventions aim to improve communication, reduce stress, enhance problem-solving skills, and support individuals with schizophrenia and their family members.

Skip To:
Learn More:
- Mental Health Treatment Rehab
- What Is A Mental Health Hospital?
- What Is Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT)?
- What Is Dialectical Behavior Therapy (DBT)?
- Dialectical Behavior Therapy vs Cognitive Behavioral Therapy
- Psychiatric Disorder Treatment, Diagnosis, & Types
- Co-Occurring Disorders Treatment Options
- Neuropsychopharmacology
- Top-Rated Mental Health Treatment Center
- Different Types of Mental Health Treatment, Diagnosis & Care
How To Help Someone With Schizophrenia Who Refuses Treatment?
Establishing a trusting and supportive relationship with the person is crucial. Show empathy, listen to their concerns, and validate their feelings. Avoid being confrontational or judgmental, as it may further alienate them. Still, if the person with schizophrenia trusts and respects someone else, such as a family member, close friend, or peer support worker, consider involving that person in discussions about treatment. Sometimes, hearing from someone they trust can positively impact and influence their decision to seek treatment.
In some cases, court-ordered treatment for schizophrenia is necessary. Suppose the person’s refusal of treatment poses a risk to their safety or the safety of others. In that case, seeking help from mental health professionals or crisis intervention services is crucial.
Top 3 Types of Schizophrenia Therapies
Schizophrenia is a complex mental disorder with subtypes based on the predominant symptoms and presentation. The Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-5), which is widely used for diagnosis, recognizes the following subtypes of schizophrenia:
- Paranoid Type: This subtype is characterized by prominent delusions and auditory hallucinations.
- Disorganized Type: This subtype is characterized by disorganized thinking, speech, and behavior.
- Catatonic Type: This subtype is characterized by prominent motor disturbances, such as immobility, excessive motor activity, rigidity, or peculiar posturing. Catatonic symptoms can include echolalia (repeating others’ words) or echopraxia (imitating others’ movements).
- Undifferentiated Type: This subtype is used when the individual’s symptoms do not fit into any specific subtype or when they exhibit a mix of symptoms from different subtypes.
- Residual Type: This subtype is used when an individual has a history of at least one episode of schizophrenia but is currently experiencing milder or residual symptoms, such as social withdrawal, flat affect, or unusual beliefs.
These subtypes are not mutually exclusive, and an individual’s presentation may change. The subtypes are primarily used for diagnostic purposes and treatment planning, as treatment approaches can vary based on symptom profiles and individual needs.
Paranoid Schizophrenia Symptoms and Treatment
The treatment approach for paranoid schizophrenia, a subtype of schizophrenia, typically involves a combination of medication and psychosocial treatment for schizophrenia. Paranoid schizophrenia symptoms include the following:
- Delusions.
- Hallucinations.
- Disorganized speech.
- Disorganized behavior.
- Reduced or lack of regular emotional expression, motivation, and ability to experience pleasure.
- Reduced speech.
- Social withdrawal.
- Diminished emotional responsiveness.
- Impaired functioning.
The treatment for paranoid schizophrenia should be tailored to the individual’s specific needs, preferences, and level of functioning. Ongoing collaboration between mental health professionals, the individual, and their support network is crucial for effective management and support throughout the treatment process.
Catatonic Schizophrenia Treatment
Catatonic schizophrenia is a subtype of schizophrenia characterized by prominent motor disturbances, such as immobility, rigidity, or repetitive movements. Here are some commonly used treatments:
- Antipsychotic medications are often prescribed to manage the symptoms of catatonic schizophrenia. Typical and atypical antipsychotics may be used, depending on the individual’s response and specific needs. Benzodiazepines, a sedative medication, may also be prescribed in some cases to help alleviate catatonic symptoms.
- In severe or treatment-resistant cases of catatonic schizophrenia, electroconvulsive therapy (ECT) may be considered. ECT involves the controlled administration of electrical currents to the brain, inducing a brief seizure. This treatment is effective in rapidly alleviating catatonic symptoms.
- Various psychosocial interventions can be beneficial in the treatment of catatonic schizophrenia. Individual therapy, such as cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT), can help individuals address distorted thoughts and improve coping strategies. Occupational therapy can assist in regaining motor skills, enhancing daily functioning, and promoting independence. Supportive counseling and psychoeducation for both the individual and their family can also help manage the impact of the illness.
- Individuals with catatonic schizophrenia may require supportive care to ensure their safety and well-being. This may involve close monitoring, assistance with activities of daily living, and creating a structured and supportive environment. In severe cases, hospitalization may be necessary for intensive treatment and stabilization.
Bipolar Disorder and Schizophrenia Treatment
Bipolar disorder and schizophrenia are distinct mental health conditions with different diagnostic criteria. Bipolar disorder is characterized by episodes of mood swings, including periods of elevated or manic mood and periods of depression. Schizophrenia, on the other hand, is a chronic and severe mental disorder characterized by symptoms such as delusions, hallucinations, disorganized thinking, and cognitive impairments.
However, if you are referring to a person who has both bipolar disorder and schizophrenia, this is sometimes referred to as schizoaffective disorder. The treatment approach for schizoaffective disorder often involves a combination of medication, psychotherapy, and psychosocial interventions.
Schizophrenia Treatment Drugs Fact Sheet
Schizophrenia Treatment Medication
Medication is a crucial component in the treatment of schizophrenia. Antipsychotic medications, also known as neuroleptics, are the main class of medications used to manage the symptoms of schizophrenia. They work by blocking or reducing the activity of dopamine receptors in the brain, which helps to alleviate psychotic symptoms such as delusions and hallucinations.
Here are some common types of antipsychotic medications used in the treatment of schizophrenia:
- First-Generation Antipsychotics (Typical Antipsychotics).
- This is the older antipsychotic treatment for schizophrenia that was developed. Examples include haloperidol (Haldol), chlorpromazine (Thorazine), and fluphenazine (Prolixin).
- Second-Generation Antipsychotics (Atypical Antipsychotics).
- These schizophrenia new treatment medications are often the first-line treatment for schizophrenia due to their effectiveness and a lower risk of specific side effects compared to first-generation antipsychotics. Examples include risperidone (Risperdal), olanzapine (Zyprexa), quetiapine (Seroquel), aripiprazole (Abilify), and clozapine (Clozaril).
- Long-Acting Injectable Antipsychotics.
- These formulations allow for administering antipsychotic medication via injections lasting for weeks or months. They can be beneficial for individuals who have difficulty with medication adherence. Examples include risperidone long-acting injection (Risperdal Consta), paliperidone palmitate (Invega Sustenna), and aripiprazole lauroxil (Aristada).
The choice of medication depends on various factors, including the individual’s symptoms, previous treatment response, side effect profile, and personal preferences.
Why is Insulin Shock Therapy for Schizophrenia Not Being Used Today?
This approach is considered outdated and is no longer a recommended or widely used treatment for schizophrenia due to its associated risks and the availability of more effective and safer treatment options. Insulin shock therapy was a historical treatment for psychiatric conditions, including schizophrenia. It involved inducing a coma by administering insulin, often in high doses.
Electroconvulsive Therapy for Schizophrenia
Electroconvulsive therapy (ECT) is a medical procedure involving inducing controlled brain seizures using electrical currents. While ECT is primarily used to treat severe depression, it can also be considered a treatment option for individuals with schizophrenia, especially when experiencing severe symptoms or not responding to other treatments.
Treatment for Schizophrenia Without Medication
While medication is a primary and the first treatment for schizophrenia, there are also non-medication approaches that can be used to support individuals with the condition.
These non-medication interventions are typically used as complementary or adjunctive treatments and are not intended to replace medication.
Here are some non-medication treatment options for schizophrenia:
- Psychotherapy.
- Different forms of psychotherapy can be beneficial in managing symptoms and improving overall functioning. Cognitive therapy for schizophrenia is one commonly used approach that helps individuals identify and challenge distorted thoughts and develop coping strategies. Other types of therapy include the following:
- Family therapy for schizophrenia.
- Art therapy for schizophrenia.
- Group therapy for schizophrenia.
- Different forms of psychotherapy can be beneficial in managing symptoms and improving overall functioning. Cognitive therapy for schizophrenia is one commonly used approach that helps individuals identify and challenge distorted thoughts and develop coping strategies. Other types of therapy include the following:
- Psychosocial Interventions.
- These interventions include social skills training, vocational rehabilitation, supported employment programs, and housing assistance. Psychosocial interventions can help individuals develop practical skills, enhance social interactions, and improve their quality of life.
- Healthy Lifestyle.
- Adopting a healthy lifestyle can contribute to overall well-being and symptom management. This includes the following:
- Maintaining a regular sleep schedule.
- Engaging in regular physical activity.
- Practicing stress reduction techniques (such as mindfulness or relaxation exercises).
- Following a nutritious diet.
- Adopting a healthy lifestyle can contribute to overall well-being and symptom management. This includes the following:
The effectiveness of non-medication treatments may vary from person to person. Moreover, regular monitoring and ongoing support are crucial for individuals with schizophrenia, regardless of the treatment approach taken.

Free Treatment Plan for Schizophrenia PDF
Embed the below “Treatment Plan for Schizophrenia PDF” to your Website. The We Level Up mental health treatment center team provides this schizophrenia treatment sample pdf. To use the above file for free, you agree to link back and attribute its source and owner at https://welevelup.com/mental-health/schizophrenia-treatment/

Get Your Life Back
Find Hope & Recovery. Get Safe Comfortable Detox, Addiction Rehab & Dual Diagnosis High-Quality Care.
Hotline(844) 597-1011Schizophrenia Treatment-Related Statistics
The prognosis of individuals undergoing schizophrenia treatment is generally unpredictable. Based on a study, around 20% of patients report favorable schizophrenia treatment outcomes. The remaining ones experience numerous psychotic episodes and poorly respond to antipsychotic medications. Moreover, there is a treatment gap in managing schizophrenia, with many individuals not receiving adequate care or experiencing delays in accessing appropriate treatment.
45-55
Schizophrenia typically emerges in late adolescence or early adulthood. However, it can occur at any age, and there may be a second onset peak in individuals aged 45-55.
Source: NCBI
2.4 Million
About 1% of the US population (approximately 2.4 million adults) is estimated to have schizophrenia.
Source: NCBI
50%
About 50% of individuals diagnosed with schizophrenia experience significant improvement, allowing them to attain independence and engage in work. Another 25% show improvement but still require support from a solid network to navigate daily life.
Source: NCBI

Dealing With Treatment Resistant Schizophrenia
While medications play a significant role, psychosocial interventions can also be valuable in managing treatment-resistant schizophrenia. Psychotherapy, such as schizophrenia cognitive therapy, can help individuals develop coping strategies, address distorted thinking patterns, and enhance overall functioning.
Psychosocial rehabilitation programs, including vocational training, social skills development, and supported employment, can assist individuals in improving their quality of life, self-esteem, and community integration.
Given the complexity of treatment-resistant schizophrenia, it is essential to consult specialists with expertise in managing such cases.
Seeking a second opinion from a psychiatrist or mental health professional experienced in treating treatment-resistant schizophrenia can provide fresh insights, alternative treatment options, or access to cutting-edge research and clinical trials.
Collaborating with a knowledgeable treatment team can help explore all available options and address the individual’s needs.
Dealing with treatment-resistant schizophrenia requires persistence, patience, and a comprehensive approach. Maintaining open and ongoing communication with healthcare providers, involving support networks, and staying informed about emerging treatment options is crucial.
While the journey may be challenging, advancements in research and ongoing efforts in mental health offer hope for individuals living with treatment-resistant schizophrenia.
Get Help. Get Better. Get Your Life Back.
Searching for Accredited Drug and Alcohol Rehab Centers Near You?
Even if you have failed previously and relapsed, or are in the middle of a difficult crisis, we stand ready to support you. Our trusted behavioral health specialists will not give up on you. When you feel ready or just want someone to speak to about therapy alternatives to change your life call us. Even if we cannot assist you, we will lead you to wherever you can get support. There is no obligation. Call our hotline today.
(844) 597-1011Understanding The Negative Symptoms of Schizophrenia Treatment
Understanding and addressing the negative symptoms of schizophrenia are crucial aspects of treatment. Negative symptoms refer to the absence or reduction of expected behaviors, emotions, and motivations in healthy individuals.
These symptoms can significantly impact an individual’s quality of life and functioning. Here are some considerations for addressing the negative symptoms of schizophrenia with different treatment methods for schizophrenia:
- Medication Adjustment: Reviewing the current medication regimen with a psychiatrist can help determine if any specific medications or therapy schizophrenia options contribute to or worsen the negative symptoms.
- Psychosocial Interventions: Psychosocial rehabilitation programs focused on vocational training, social integration, and meaningful activities can also improve functioning and overall well-being.
- Family Education and Support: Involving family members or caregivers in the treatment process can provide crucial support and understanding. Education about negative symptoms can help them better recognize and respond to the individual’s needs. Family support groups can also offer a space for sharing experiences and learning from others facing similar challenges.

- Physical Health and Lifestyle: Attention to physical and overall well-being can positively impact negative symptoms. Encouraging regular exercise, maintaining a healthy diet, and ensuring adequate sleep can help improve energy levels, mood, and overall functioning.
- Collaborative Treatment Planning: Collaborating with healthcare professionals to develop an individualized treatment plan is essential. This involves ongoing communication, regular monitoring of symptoms, and adjustments as needed. Open and honest discussions with the treatment team can help ensure that the focus is not solely on positive symptoms but also on addressing negative symptoms and enhancing the overall quality of life.
Understanding and addressing the negative symptoms of schizophrenia require a holistic approach that combines medication management, psychosocial interventions, and support from loved ones.
First-class Facilities & Amenities
World-class High-Quality Addiction & Mental Health Rehabilitation Treatment
Rehab Centers TourRenowned Addiction Centers. Serene Private Facilities. Inpatient rehab programs vary.
Addiction Helpline(844) 597-1011Proven recovery success experience, backed by a Team w/ History of:
15+
Years of Unified Experience
100s
5-Star Reviews Across Our Centers
10K
Recovery Success Stories Across Our Network
- Low Patient to Therapist Ratio
- Onsite Medical Detox Center
- Comprehensive Dual-Diagnosis Treatment
- Complimentary Family & Alumni Programs
- Coaching, Recovery & Personal Development Events
How To Find Schizophrenia Treatment Centers Near Me?
Are you searching for schizophrenia treatment centers in Los Angeles, Florida, or near you? Remember, when searching for treatment centers, consider factors such as location, specialized programs, treatment approaches, and the availability of comprehensive services. It’s essential to research and gather as much information as possible to decide on the best treatment center for your needs.
To find treatment options schizophrenia resources and “treatment centers for schizophrenia near me,” there are several steps you can take:
- Consult with Healthcare Providers: Contact your primary care physician or psychiatrist. They can provide recommendations or referrals to specialized treatment centers or mental health professionals who have experience in treating schizophrenia. They may have a network of resources or be familiar with local treatment centers that can meet your specific needs.
- Utilize Online Directories: Online directories or databases can be helpful tools in locating treatment centers near your location. Websites such as the Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration (SAMHSA) Treatment Locator (https://findtreatment.samhsa.gov/).
- Contact Mental Health Helplines or Hotlines: Mental health helplines or hotlines can provide information, support, and guidance in finding treatment centers. They often have resources and databases readily available and can connect you to appropriate treatment options in your area. Helplines such as the National Alliance on Mental Illness (NAMI) helpline (1-800-950-NAMI) or the SAMHSA National Helpline (1-800-662-HELP) can be valuable resources.
- Reach Out to Local Mental Health Organizations: Local mental health organizations or advocacy groups may have information about treatment centers specializing in schizophrenia or can provide guidance on where to seek help. They often have regional resources or directories that can assist in finding suitable treatment options.
- Consult with Insurance Provider: If you have health insurance, contacting your insurance provider can help identify treatment centers covered by your plan. They can list in-network providers or “schizophrenia treatment near me” specializing in schizophrenia treatment.
We Level Up Residential Treatment for Schizophrenia
Inpatient rehabilitation programs for schizophrenia treatment provide intensive care and support within a structured and supervised environment. These programs address acute symptoms, stabilize individuals, and facilitate their transition back to community living.
Here at We Level Up mental health treatment center, we offer round-the-clock monitoring and support from a multidisciplinary team of healthcare professionals, including psychiatrists, nurses, therapists, and support staff. This constant presence ensures immediate intervention and response to emergent or worsening symptoms.
Residential treatment centers for schizophrenia focus on optimizing medication regimens, often through close collaboration with psychiatrists. This includes medication evaluation, adjustment, and monitoring to control symptoms and minimize side effects. Medication adherence is closely monitored and supported during the inpatient stay.
Living with schizophrenia can present unique challenges, but individuals can lead fulfilling lives with proper treatment, support, and self-care. Individuals with schizophrenia must advocate for themselves, stay informed about their condition, and work closely with healthcare professionals to develop personalized strategies for managing treatment and schizophrenia symptoms and achieving their goals.
If you don’t know where to start or are looking for treatment options, connect with We Level Up mental health treatment center for resources.
World-class, Accredited, 5-Star Reviewed, Effective Addiction & Mental Health Programs. Complete Behavioral Health Inpatient Rehab, Detox plus Co-occuring Disorders Therapy.
CALL(844) 597-1011End the Addiction Pain. End the Emotional Rollercoaster. Get Your Life Back. Start Drug, Alcohol & Dual Diagnosis Mental Health Treatment Now. Get Free No-obligation Guidance by Substance Abuse Specialists Who Understand Addiction & Mental Health Recovery & Know How to Help.
Top 5 Treatments of Schizophrenia FAQs
-
What is the treatment for schizophrenia?
Treating schizophrenia typically involves a combination of medication, such as antipsychotic drugs, and psychosocial interventions. Medications help manage the symptoms of schizophrenia, while psychosocial interventions, including therapy, social support, and skills training, help individuals develop coping strategies, improve functioning, and enhance their overall quality of life.
-
Is there treatment for schizophrenia?
Yes, there is treatment available for schizophrenia. While there is no cure for the condition or considered the best treatment for schizophrenia, a combination of medication, therapy, and psychosocial interventions can effectively manage symptoms, improve functioning, and support individuals in leading fulfilling lives despite the challenges of schizophrenia.
-
What is the best schizophrenia natural treatment?
Natural treatments alone may not be sufficient to manage schizophrenia effectively. However, adopting a holistic approach that includes lifestyle modifications, such as regular exercise, maintaining a healthy diet, managing stress, getting adequate sleep, and engaging in supportive social relationships, can complement conventional treatment and promote overall well-being for individuals with schizophrenia. It’s crucial to consult a healthcare professional to develop therapeutic treatment for schizophrenia tailored to individual needs.
-
What are the new treatments for schizophrenia?
Some emerging schizophrenia latest treatment approaches include targeted medications, such as glutamatergic agents, and innovative therapies like transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS) and virtual reality-based interventions. However, further research is needed to establish the new schizophrenia treatments’ effectiveness and safety. It’s essential to stay updated with current scientific advancements and consult with healthcare professionals to explore the most up-to-date treatment options available.
-
What is the best therapy for schizophrenia?
The best therapy for schizophrenia typically involves a combination of approaches tailored to the individual’s needs. However, cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) has shown promise in helping individuals with schizophrenia manage symptoms and improve functioning. CBT identifies and challenges distorted thoughts and beliefs, develops coping strategies, and enhances problem-solving skills. Other therapies, such as family therapy, social skills training, and supportive therapy, can also be beneficial in addressing specific areas of concern and providing additional support. It is essential to work with a qualified mental health professional who can assess individual needs and recommend the most appropriate therapy or combination of therapies for the individual with schizophrenia.
“You’re born for a purpose!!” Motivational Mental Health Quotes. Best Quotes about Mental Health.
Schizophrenia is a complex mental health condition; seeking assistance is essential for managing symptoms and improving overall well-being.
By seeking help, you demonstrate strength and resilience. It shows that you are willing to confront the challenges associated with schizophrenia and take control of your mental health. Treatment options, including schizophrenia therapy, medication, support groups, and lifestyle changes, can significantly enhance your quality of life.
Get FREE mental health treatment insurance check – https://welevelup.com/rehab-insurance/
If you or a loved one is struggling with schizophrenia or other mental health disorder(s), call for a FREE consultation 24/7 at (561) 678-0917
Experience Transformative Recovery at We Level Up Treatment Centers.
See our authentic success stories. Get inspired. Get the help you deserve.
Start a New Life
Begin with a free call to an addiction & behavioral health treatment advisor. Learn more about our dual-diagnosis programs. The We Level Up Treatment Center Network delivers recovery programs that vary by each treatment facility. Call to learn more.
- Personalized Care
- Caring Accountable Staff
- World-class Amenities
- Licensed & Accredited
- Renowned w/ 100s 5-Star Reviews
We’ll Call You
Search We Level Up Schizophrenia Treatment, Mental Health Topics & Resources
Sources
[1] Schizophrenia – NIMH Available from: https://www.nimh.nih.gov/health/topics/schizophrenia
[2] Hany M, Rehman B, Azhar Y, et al. Schizophrenia. [Updated 2023 Mar 20]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2023 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK539864/
[3] Patel KR, Cherian J, Gohil K, Atkinson D. Schizophrenia: overview and treatment options. P T. 2014 Sep;39(9):638-45. PMID: 25210417; PMCID: PMC4159061.
[4] What is Schizophrenia? – Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration (SAMHSA)
[5] Schizophrenia WHO Available from: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/schizophrenia
[6] Schizophrenia: Overview – Healthy People 2030 Available from: https://health.gov/healthypeople/tools-action/browse-evidence-based-resources/schizophrenia-overview
[7] Schizophrenia – VA Mental Health – Veterans Affairs (.gov)
[8] Inpatient Evaluation of Adults With Schizophrenia – Clinical Trials (.gov)
[9] Definition of psychosis – NCI Dictionary of Cancer Terms
[10] Schizophrenia and the Law – Office of Justice Programs (.gov)


