The Endocrine System
Alcohol has widespread effects on multiple organs, including the endocrine organs, potentially impairing endocrine function. What is the endocrine system? The endocrine system is a network of organs and glands throughout the body. It’s similar to the nervous system in that it plays an important role in regulating and controlling many of the body’s functions. However, while the nervous system uses neurotransmitters and nerve impulses for communication, the endocrine system uses chemical messengers called hormones [1].
Hormones are produced by the endocrine system’s glands, traveling through the bloodstream to various tissues and organs in the body. The hormones then tell these tissues and organs what to do or how to function. Some examples of bodily functions that are controlled by the endocrine system include:
- Metabolism
- Appetite
- Growth and development
- Sexual function and reproduction
- Heart rate
- Blood pressure
- Sleeping and waking cycles
- Body temperature
The endocrine system ensures proper communication between different body organs to maintain a constant internal environment, also called homeostasis. The endocrine system also plays an essential role in enabling the body to respond and appropriately cope with changes in the external and internal environments, such as response to stress and injury [2].
Organs in the Endocrine System
The endocrine system’s glands are where hormones are produced, stored, and released. Each gland produces one or more hormones, which target specific organs and tissues in the body.
The glands of the endocrine system include the:
Pituitary. The pituitary gland is located below the hypothalamus, and the hormones it produces affect reproduction and growth. They can also control the function of other endocrine glands.
Hypothalamus. While some people don’t consider it a gland, the hypothalamus produces multiple hormones that control the pituitary gland. It regulates many functions, including body temperature, sleep-wake cycles, and appetite. It can also regulate the function of other endocrine glands.
Pineal. This gland is found in the middle of your brain. It’s important for your sleep-wake cycles.
Thyroid. The thyroid gland is located in the front part of your neck. It’s very important for metabolism.
Parathyroid. Also located in the front of your neck, the parathyroid gland is important for maintaining control of calcium levels in your bones and blood.
Adrenal. One adrenal gland can be found on top of each kidney. These glands produce hormones that are important for regulating functions such as heart rate, blood pressure, and stress response.
Thymus. Located in the upper torso, the thymus is active until puberty and produces hormones important for developing a type of white blood cell called a T cell.
Pancreas. The pancreas is located in your abdomen behind your stomach. Its endocrine function involves controlling blood sugar levels.
Some endocrine glands also have non-endocrine functions. For instance, the testes and ovaries produce hormones but have the non-endocrine function of making eggs and sperm.

Get Your Life Back
Find Hope & Recovery. Get Safe Comfortable Detox, Addiction Rehab & Dual Diagnosis High-Quality Care.
Hotline(844) 597-1011How Does Alcohol Affect The Endocrine System?
Chronic consumption of alcohol disrupts the communication between the endocrine, nervous, and immune systems, causing hormonal imbalances that lead to severe and profound consequences at the physiological and behavioral levels.
These alcohol-induced hormonal dysregulations affect the entire body. They can lead to various disorders such as reproductive deficits, stress abnormalities, body growth disorders, cancer, thyroid problems, immune disorders, bone diseases, and behavioral and psychological disorders.
Alcohol and its metabolite acetaldehyde directly affect cell membranes and influence intracellular metabolism. Indirect effects of alcohol on the endocrine system include nausea, stress, and vomiting during acute intoxication and alcohol withdrawal. Whereas the list of alcohol-induced endocrine dysfunction is long, epidemiological and scientific evidence is frequently controversial.
Controversies may result from the highly heterogenic group of alcohol-dependent individuals regarding duration and dose of alcohol consumption, periods of abstinence, gender, age, nutritional status, use of other drugs, cigarette smoking, presence of other diseases, particularly liver disease, and the complexity of endocrine regulation in general.
Alcohol Effects on Endocrine System
Alcohol has the power to hinder glands linked with the regulation and secretion of hormones, like the pituitary gland, possibly leading to complications with the body’s ability to maintain hormonal equilibrium. The pituitary gland, for instance, synthesizes and secretes essential healing and repair hormones, such as human growth hormone (HGH). This gland has been shown to experience noticeable impairment from alcohol consumption.
Insulin, an important hormone that regulates blood sugar, can be severely affected by prolonged alcohol consumption. After heavy alcohol consumption, blood sugar often spikes dramatically. Insulin comes to the rescue by transporting this sugar (blood glucose) into the cells to be used as energy. When blood sugar spikes in a robust, dramatic motion, insulin will quickly bring it down similarly, typically resulting in low blood sugar. This can be particularly dangerous for type 2 diabetics, who are already at odds with maintaining normal blood sugar levels.
Alcohol and type 2 diabetes are closely linked. Chronic heavy consumption of alcohol deteriorates glucose tolerance and insulin resistance, which may well be one of the mechanisms involved in the malignant effect of alcohol about the development of diabetes.

Alcohol also can impede the body’s ability to regulate and absorb calcium, creating a strong risk factor for the development of osteoporosis. Long-term health concerns such as liver damage, ulcers, and sexual dysfunction typically result from chronic or acute consumption.
The thyroid is an endocrine gland. Its location is in the inferior, anterior neck, responsible for the formation and secretion of thyroid hormones and iodine homeostasis within the human body. Does alcohol affect thyroid levels? Yes. It has been reported to cause direct suppression of thyroid function by cellular toxicity and indirect suppression by blunting thyrotropin-releasing hormone response. It causes a decrease in peripheral thyroid hormones during chronic use and alcohol withdrawal. Alcohol use may also confer protective effects against thyroid nodularity, goiter, and thyroid cancer.
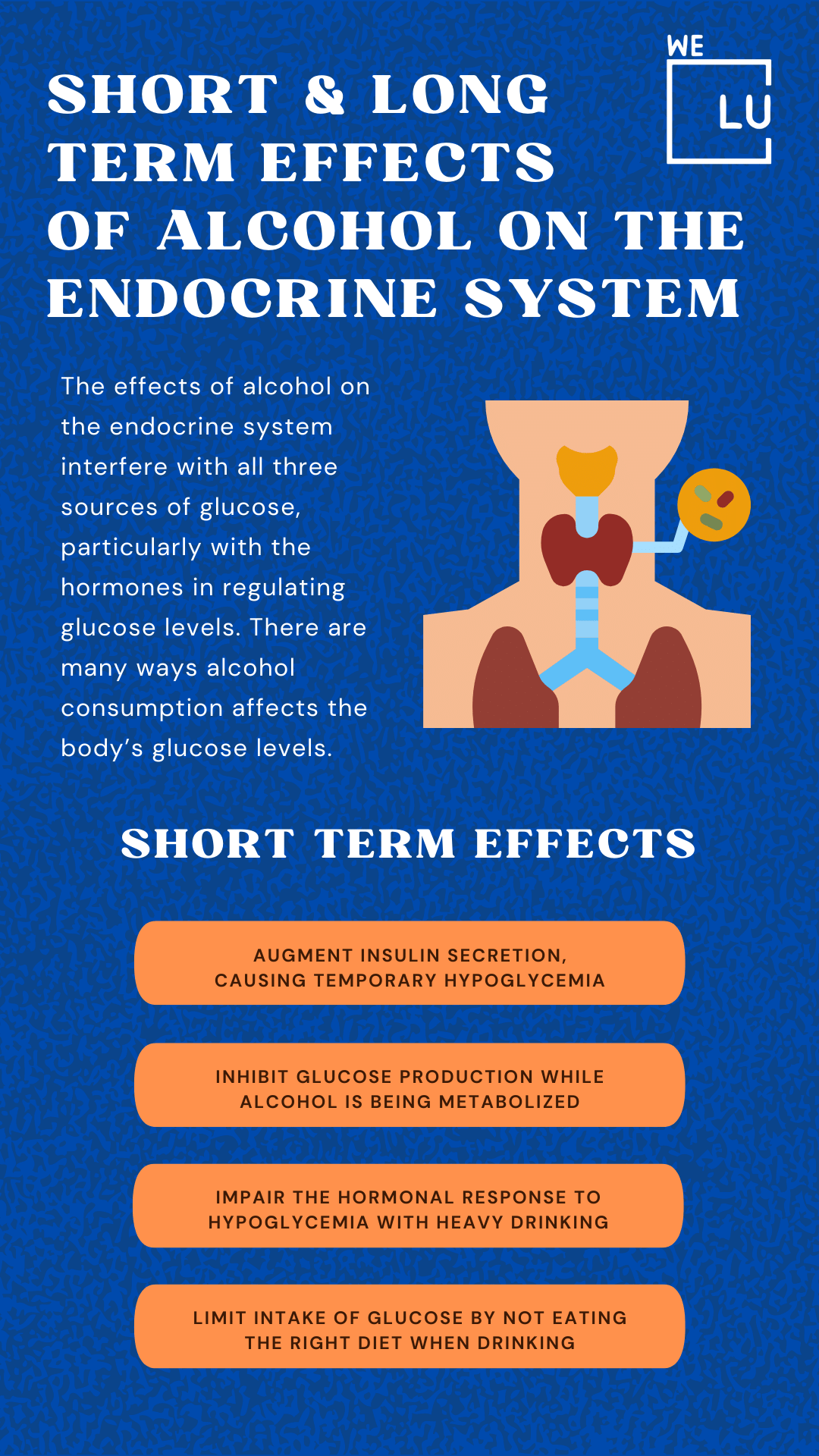
Short-Term Effects of Alcohol on the Endocrine System
The effects of alcohol on the endocrine system interfere with all three sources of glucose, particularly with the hormones regulating glucose levels. There are many ways alcohol consumption affects the body’s glucose levels. Alcohol is known to:
- Augment insulin secretion, causing temporary hypoglycemia
- Inhibit glucose production while alcohol is being metabolized
- Impair the hormonal response to hypoglycemia with heavy drinking
- Limit intake of glucose by not eating the right diet when drinking
Get Help. Get Better. Get Your Life Back.
Searching for Accredited Drug and Alcohol Rehab Centers Near You?
Even if you have failed previously and relapsed, or are in the middle of a difficult crisis, we stand ready to support you. Our trusted behavioral health specialists will not give up on you. When you feel ready or just want someone to speak to about therapy alternatives to change your life call us. Even if we cannot assist you, we will lead you to wherever you can get support. There is no obligation. Call our hotline today.
(844) 597-1011Long-Term Effects of Alcohol on the Endocrine System
Blood Sugar Levels
Chronic heavy alcohol consumption can increase the body’s glucose levels. Chronic heavy drinking can cause glucose intolerance in healthy people. It can also:
- Alter the effectiveness of medications for diabetes
- Lower survival rates for alcoholics with diabetes
- Cause both hypoglycemic and hyperglycemic episodes in alcoholics
- Increase secretion of glucagon and other hormones that raise glucose levels
- Reduce the body’s responsiveness to insulin
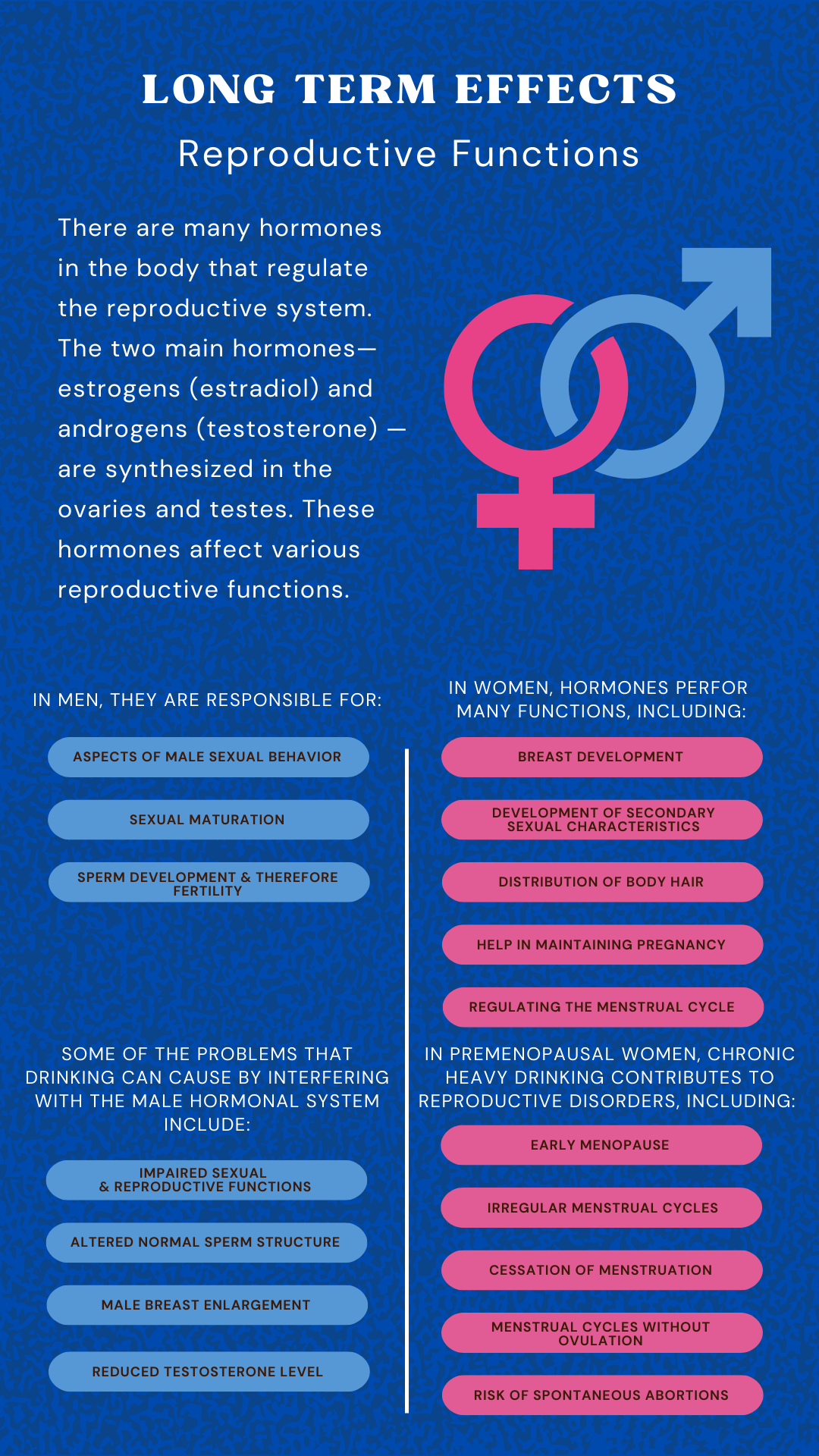
Reproductive Functions
Many hormones in the body regulate the reproductive system. The two main hormones—estrogens (estradiol) and androgens (testosterone) —are synthesized in the ovaries and testes. These hormones affect various reproductive functions.
In men, they are responsible for:
- Aspects of male sexual behavior
- Sexual maturation
- Sperm development and, therefore, fertility
In women, hormones perform many functions, including:
- Breast development
- Development of secondary sexual characteristics
- Distribution of body hair
- Help in maintaining pregnancy
- Regulating the menstrual cycle
Some of the problems that drinking can cause by interfering with the male hormonal system include:
- Impaired sexual and reproductive functions
- Altered normal sperm structure
- Male breast enlargement
- Reduced testosterone level
Although many reproductive problems were found in women who were alcoholics, some issues were also found in women considered social drinkers. In premenopausal women, chronic heavy drinking contributes to reproductive disorders, including:
- Early menopause
- Irregular menstrual cycles
- Cessation of menstruation
- Menstrual cycles without ovulation
- Risk of spontaneous abortions
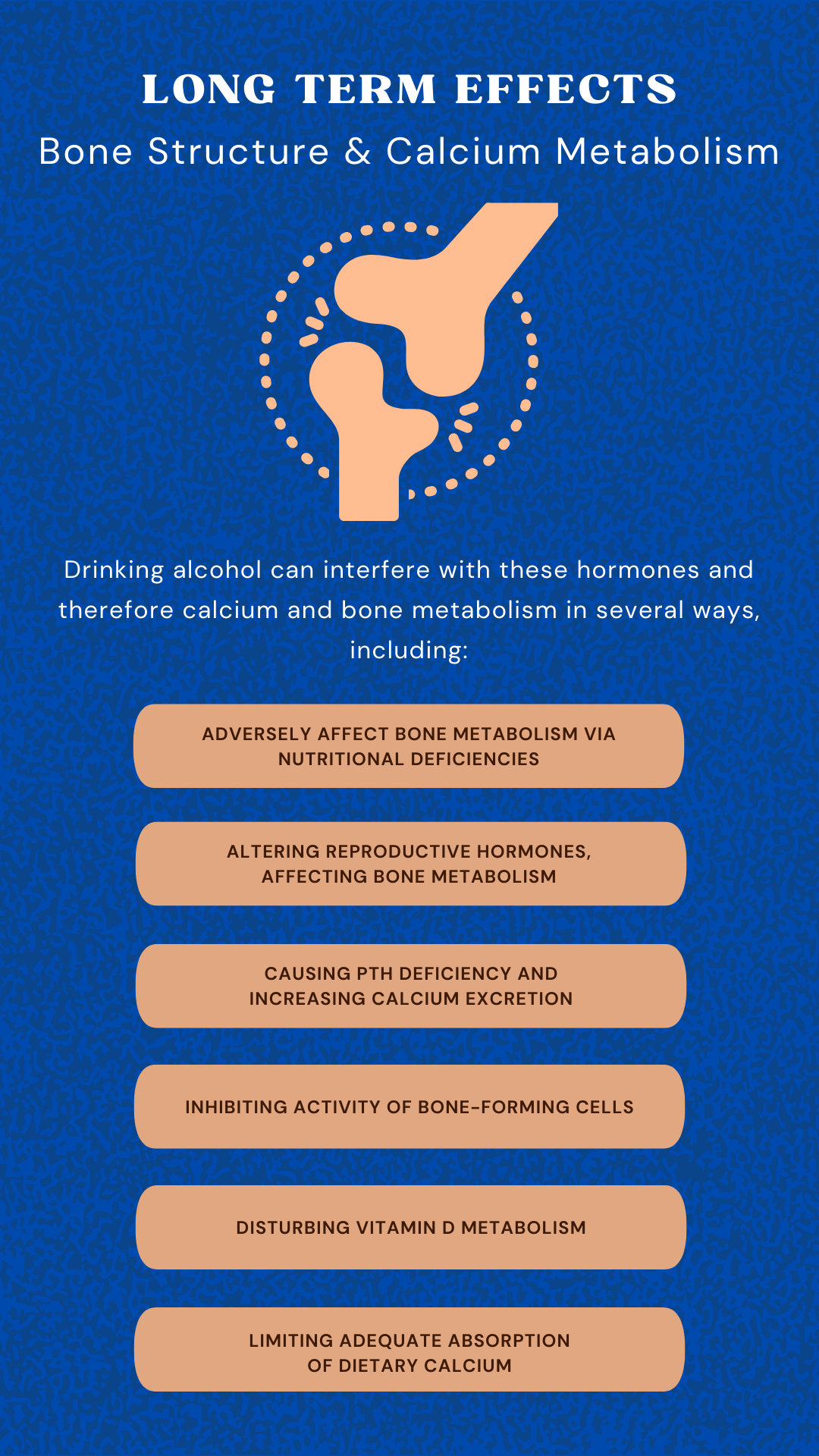
Bone Structure and Calcium Metabolism
Hormones play an important function in maintaining calcium levels in the body, which is necessary not only for strong teeth and bones but also for communication between and within cells of the body. Several hormones—vitamin D-derived hormones, parathyroid hormone (PTH), and calcitonin—regulate calcium absorption, excretion, and distribution between bones and body fluids.
Drinking alcohol can interfere with these hormones and, therefore, calcium and bone metabolism in several ways, including:
- Adversely affect bone metabolism via nutritional deficiencies
- Altering reproductive hormones, affecting bone metabolism
- Causing PTH deficiency and increasing calcium excretion
- Inhibiting activity of bone-forming cells
- Disturbing vitamin D metabolism
- Limiting adequate absorption of dietary calcium
These problems can cause calcium deficiency, leading to bone diseases, such as osteoporosis, a loss of bone mass, and therefore an increased risk of fractures.
First-class Facilities & Amenities
World-class High-Quality Addiction & Mental Health Rehabilitation Treatment
Rehab Centers TourRenowned Addiction Centers. Serene Private Facilities. Inpatient rehab programs vary.
Addiction Helpline(844) 597-1011Proven recovery success experience, backed by a Team w/ History of:
15+
Years of Unified Experience
100s
5-Star Reviews Across Our Centers
10K
Recovery Success Stories Across Our Network
- Low Patient to Therapist Ratio
- Onsite Medical Detox Center
- Comprehensive Dual-Diagnosis Treatment
- Complimentary Family & Alumni Programs
- Coaching, Recovery & Personal Development Events
Alcohol Abuse Statistics
Alcohol use disorder (AUD) replaced the designations that had previously been separately defined as “alcohol abuse” and “alcohol dependence.” According to the National Institutes of Health (NIH), an alcohol use disorder (AUD) is defined as a “chronic relapsing brain disease” that causes a person to drink compulsively despite adverse consequences to daily life and overall health.
Roughly 15 million people in the United States were diagnosed with an alcohol use disorder in 2018, including 19.2 million men, 5.3 million women, and 401,000 adolescents ages 12–17.
Alcohol Abuse Statistics According to the Center for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC)
- Percent of adults aged 18 and over who had at least one heavy drinking day (five or more drinks for men and four or more drinks for women) in the past year: 25.1% [3]
- Number of alcoholic liver disease deaths: 29,505
- Alcoholic liver disease deaths per 100,000 population: 9.0
- Number of alcohol-induced deaths, excluding accidents and homicides: 49,061
- Alcohol-induced deaths, excluding accidents and homicides per 100,000 population: 14.9
Alcohol Abuse Statistics According to the World Health Organization (WHO)
- Worldwide, 3 million deaths every year result from the harmful use of alcohol. This represents 5.3% of all deaths [4].
- The harmful use of alcohol is a causal factor in more than 200 disease and injury conditions.
- Overall, 5.1% of the global burden of disease and injury is attributable to alcohol, as measured in disability-adjusted life years (DALYs).
- There is a causal relationship between harmful use of alcohol and a range of mental and behavioral disorders, other noncommunicable conditions, and injuries.
Alcohol Abuse Statistics According to the National Institute of Health (NIH)
- Drinking causes distress and harm. Alcohol use disorder (AUD) can range from mild to severe. Severe AUD is sometimes called alcoholism or alcohol dependence [5]
- Alcohol use disorder is a disease that causes:
- Craving – a strong need to drink
- Loss of control – not being able to stop drinking once you’ve started
- Negative emotional state – feeling anxious and irritable when you are not drinking
- Binge drinking is drinking so much at once that your blood alcohol concentration (BAC) level is 0.08% or more. For a man, this usually happens after having five or more drinks within a few hours. For a woman, it is after about 4 or more drinks within a few hours. Not everyone who binges drinks has an AUD, but they are at higher risk of getting one.
- Too much alcohol is dangerous. Heavy drinking can increase the risk of certain cancers. It may lead to liver diseases, such as fatty liver disease, alcoholic hepatitis, and alcoholic cirrhosis. It can also cause damage to the brain (wet brain) and other organs. Drinking during pregnancy can harm your baby. Alcohol also increases the risk of death from car crashes, injuries, homicide, and suicide.
World-class, Accredited, 5-Star Reviewed, Effective Addiction & Mental Health Programs. Complete Behavioral Health Inpatient Rehab, Detox plus Co-occuring Disorders Therapy.
CALL(844) 597-1011End the Addiction Pain. End the Emotional Rollercoaster. Get Your Life Back. Start Drug, Alcohol & Dual Diagnosis Mental Health Treatment Now. Get Free No-obligation Guidance by Substance Abuse Specialists Who Understand Addiction & Mental Health Recovery & Know How to Help.
Alcohol Abuse Treatment Options
There is a strong link between mental health and alcohol abuse. Individuals who struggle with mood disorders like depression and anxiety are more susceptible to developing an addiction to drugs or alcohol, often to self-medicate symptoms of their underlying mental health condition. To determine the most effective ways to alcohol addiction, it’s crucial first to get an accurate assessment of all the symptoms. When a mental health professional has evaluated the symptoms, it may be determined that another form of mental condition is present and needs a particular treatment. Very often, some combination of psychotherapy, medication, and/or lifestyle changes are effective for coping with functional.
Medically-Assisted Detox
Detox is often considered the first stage of treatment. It will help you navigate the complicated withdrawal process but doesn’t address patterns of thought and behavior contributing to drug abuse. Various treatment approaches and settings can help provide the ongoing support necessary to maintain long-term sobriety after you complete detox.
Cravings are very common during detox and can be challenging to overcome. This often leads to relapse. Constant medical care provided during inpatient treatment helps prevent relapse. Clinicians can provide necessary medication and medical expertise to lessen cravings and the effects of withdrawals.
Psychotherapy for Depression and Anxiety
Several different modalities of psychotherapy have been used in the treatment of depression, including:
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) – is an effective treatment that involves changing both the patterns of negative thoughts and the behavioral routines which are affecting the daily life of the depressed person for various forms of depression.
- Dialectical Behavior Therapy – is a comprehensive mental health and substance abuse treatment program whose ultimate goal is to aid patients in their efforts to build a life worth living. The main goal of DBT is to help a person develop what is referred to as a “clear mind.”
- Person-Centered Therapy – is a strategy that allows and encourages clients to understand and resolve their concerns in a safe, supportive environment.
- Solution–focused therapy – is an approach interested in solutions that can be quickly implemented with a simple first step leading to further positive consequences.
Dual Diagnosis Treatment
Substance abuse and mental health disorders often co-occur. In many cases, traumatic experiences can result in a mental health disorder and substance abuse. Dual diagnosis rehabilitation treats both of these issues together. The best approach for the treatment of dual diagnosis is an integrated system. This strategy treats both the substance abuse problem and the mental disorder simultaneously. Regardless of which diagnosis (mental health or substance abuse problem) came first, long-term recovery will depend largely on the treatment for both disorders done by the same team or provider.
Medication-Assisted Treatments
Medication-Assisted Treatments (MAT) for substance use and mental health disorders are commonly used in conjunction with one another. This includes the use of medications and other medical procedures. During your rehab, the staff from your treatment facility will help you identify what caused your addiction and teach you skills that will help you change your behavior patterns and challenge the negative thoughts that led to your addiction. Sometimes, the pressures and problems in your life lead you to rely on substances to help you forget about them momentarily.
Individual and Group Counseling
Addiction and mental health counseling occur in both individual and group settings. One-on-one treatment sessions may address unresolved trauma, unconscious conflicts, and specific struggles, while group sessions often involve training in life skills, stress management, conflict resolution, and social connections. Group counseling also allows clients to share their thoughts and experiences to develop social support, which is essential for lasting recovery. If you or someone you know is experiencing the effects of alcohol on the endocrine system, it is crucial to intervene early. We Level Up has addiction specialists that are standing by to help.

Experience Transformative Recovery at We Level Up Treatment Centers.
See our authentic success stories. Get inspired. Get the help you deserve.
Start a New Life
Begin with a free call to an addiction & behavioral health treatment advisor. Learn more about our dual-diagnosis programs. The We Level Up Treatment Center Network delivers recovery programs that vary by each treatment facility. Call to learn more.
- Personalized Care
- Caring Accountable Staff
- World-class Amenities
- Licensed & Accredited
- Renowned w/ 100s 5-Star Reviews
We’ll Call You
Sources:
[1] NCBI – https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3767933/
[2} NCBI – https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/6361409/
[3] CDC – https://www.cdc.gov/nchs/fastats/alcohol.htm
[4] WHO – https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/alcohol
[5] NIH – https://medlineplus.gov/alcoholusedisorderaud.html
[6] Alcohol Withdrawal Symptoms – We Level Up NJ